Figure 7.
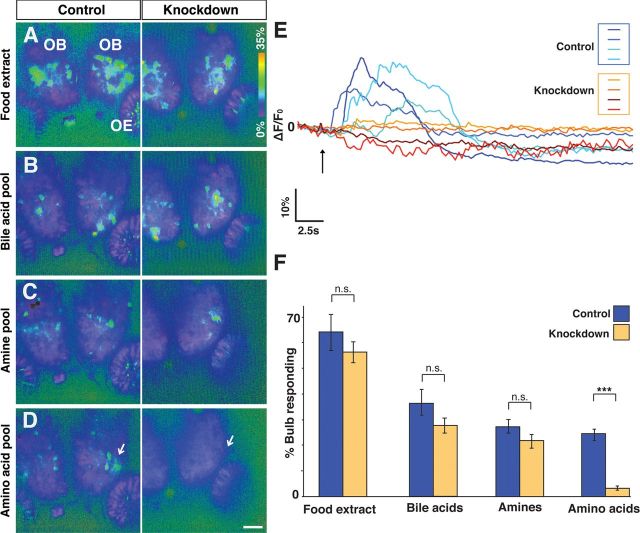
Effects of OlfCc1 knockdown are specific to amino acid-evoked activity. Transgenic HuC-Gal4;UAS-GCaMP embryos previously injected with perfect match (“Knockdown”) or mismatch (“Control”) OlfCc1 morpholino antisense oligonucleotides were assayed at 4.5 dpf for odorant-stimulated activity in the olfactory bulb. A–D, Activity heat maps are shown for two representative fish in response to food extract (A), bile acid pool (B), amine pool (C), and amino acid pool (D). Heat maps of DeltaF/F0 represent data acquired from a single optical plane and spanning the peak response (see Materials and Methods). Activity in response to food extract, bile acids, and amines is broad in the olfactory bulb and persists in the OlfCc1 knockdown. In contrast, amino acids elicit activity mainly in a cluster of lateral glomeruli (D, arrows); this activity is greatly diminished in the OlfCc1 knockdown. E, Representative DeltaF/F0 traces from ROIs corresponding to anatomically equivalent lateral glomerular cluster in 4 control fish (blue lines) and 4 knockdown fish (orange lines) after exposure (arrow) to the 9 amino acid pool. F, The area of olfactory bulb exhibiting significant activity above background was calculated and expressed as a percentage of the total area within a given optical section. Data were acquired from 14 control and 14 knockdown fish. Histograms represent mean percentages ± SEM. No significant difference was found between control and knockdown groups in response to food extract, bile acids, or amine stimuli (n.s., Not significant; p > 0.1, two-tailed Student's t test). In contrast, a highly significant difference was found between these two groups in their responses to amino acids (***p < 0.001).