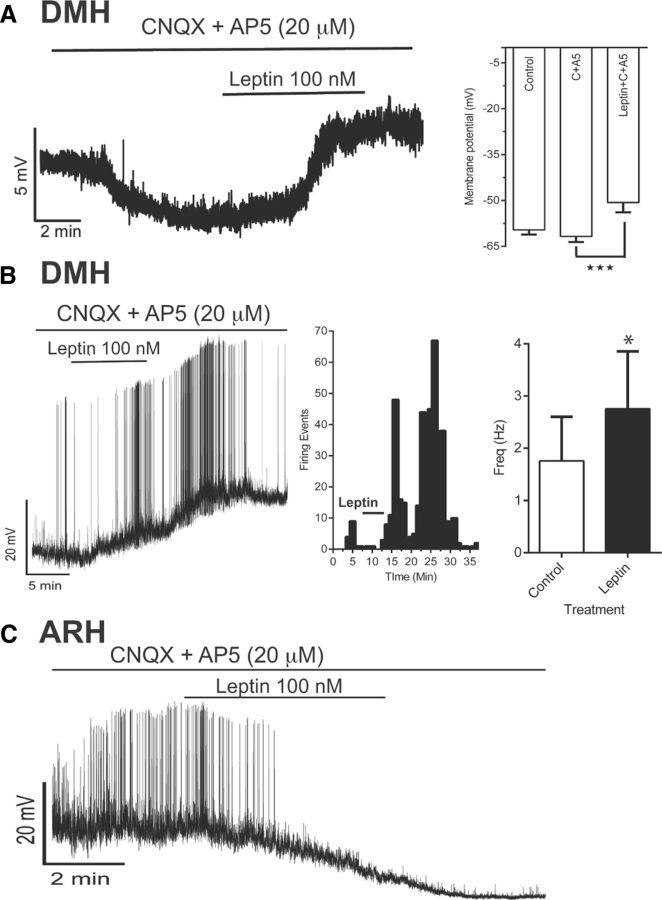
Figure 5.
Leptin induces postsynaptic depolarization and increased firing frequency in DMH NPY neurons. A. Left, Representative tracing for a current-clamp recording of DMH NPY neurons from a DIO animal. Right, Analysis of average change in membrane potential with different treatments (n = 16, 4 nonresponders, 6 animals; ANOVA; p = 0.0004). B, Left, Example of current-clamp recording demonstrating increased spontaneous action potential firing and depolarization of DMH NPY neurons after leptin treatment. Middle, Histogram showing number of firing events per minute. Right, Bar graph showing analysis of firing frequency before and after leptin exposure (paired t test, p = 0.0097; n = 12 with 5 responders). C, Example of current-clamp recording demonstrating suppressed spontaneous action potential firing and hyperpolarization of ARH NPY neurons after leptin treatment, postsynaptically (53.1 ± 1.1 mV to −62.1 ± 2.3 mV; n = 3).