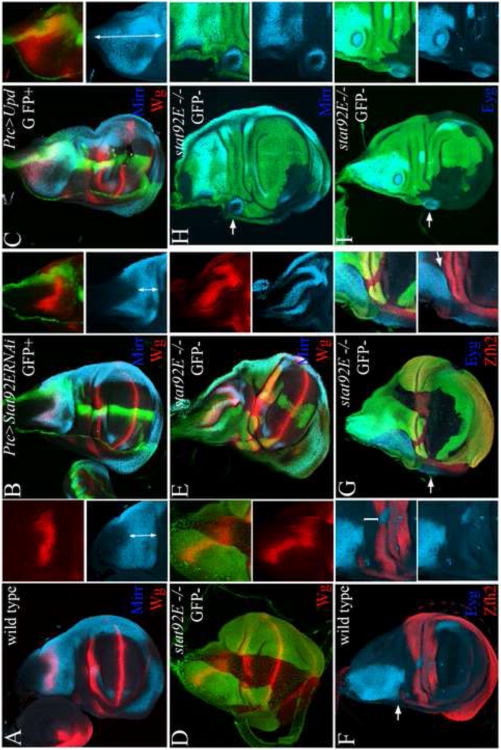
Figure 5. stat92E restricts the expansion of the medial notum and specifies the dorsal pleura cell-autonomously.
(A) Mirr (cyan) is expressed in the lateral notum and Wg (red) in the lateral notum along the border with the medial notum. (B) Depletion of Stat92E activity in the Ptc domain (green) displaced the Mirr and Wg domains toward the hinge. (C) Expression of upd in the Ptc domain resulted in the opposite displacement of the Mirr and Wg domains toward the disc stalk. Double arrows demarcate the scope of the lateral notum marked with Mirr in A-C. To quantify the effects, we measured the scope of the lateral notum relative to scope of the entire notum ML axis and found that a reduction in Ptc>StatRNAi (0.275 +/− 0.05 SE, N=7) and expansion in Ptc>Upd (0.86 +/− 0.1 SE, N=6) compared to wild type (0.395 +/− 0.5 SE, N=8). (D-E) The Wg and Mirr expression domains were also displaced laterally in stat92E mutant clones. (F) Eyg (cyan) is expressed in the notum in a broad anterior domain, and Zfh2 (red) is expressed in the hinge. An intervening domain separates the Eyg and Zfh2 domains (bracket in inset in F). Only along the anterior margin the Eyg and Zfh2 domains are adjacent (arrow in F). (G-I) In large stat92E clones that spanned the Eyg and Zfh2 domains, the intervening domain between the Eyg and Zfh2 domains was missing (arrow in inset in G). In addition, the Eyg domain was displaced laterally into the pleura (arrow in G). (H) Mirr was expressed ectopically in stat92E mutant clones laterally to the Mirr domain along the wing margin (arrow). (I) Eyg was expressed ectopically in stat92E mutant clones in the dorsal pleura (arrows).