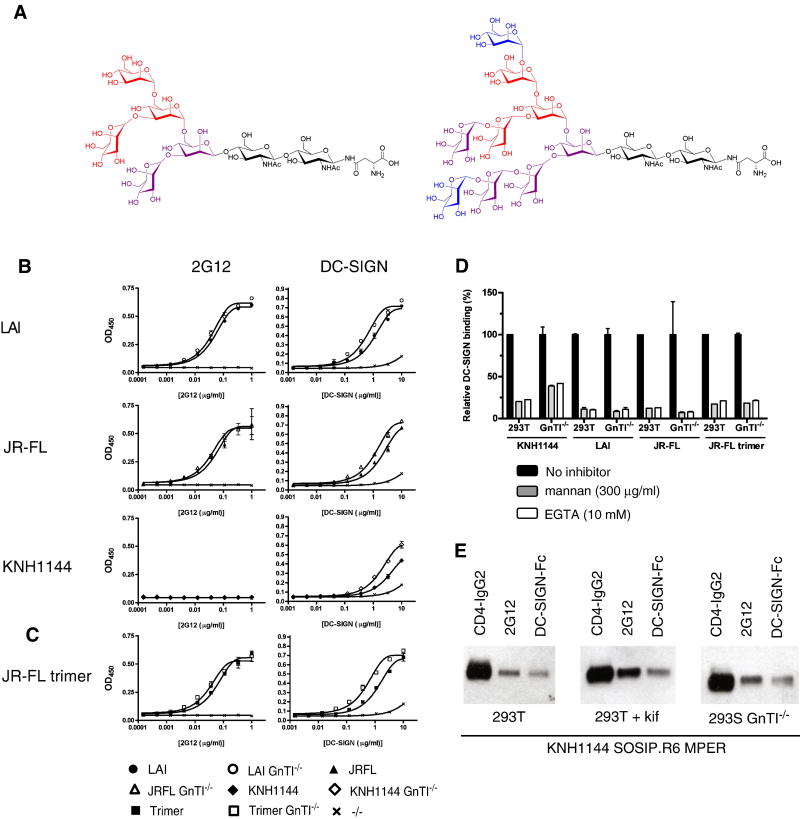
Figure 5.
Interactions with 2G12 and DC-SIGN of gp120 and gp140 proteins lacking complex N-glycans. (A) Chemical structures of Man5GlcNAc2 (left) and Man9GlcNAc2 (right) N-glycans commonly found on proteins expressed in 293S GnTI-/- cells, and in kifunensine-treated 293T cells, respectively (Elbein et al., 1990; Reeves et al., 2002). The individual mannoses that are involved in 2G12 binding (blue) and DC-SIGN binding (core binding site: red; additional contacts: burgundy and blue) are indicated (Calarese et al., 2005; Calarese et al., 2003; Feinberg et al., 2007; Feinberg et al., 2001; Guo et al., 2004; Scanlan et al., 2002; van Liempt et al., 2006). The sugar linkages are also shown. (B) Binding of 2G12 and DC-SIGN to three different gp120s produced in 293T or 293S GnTI-/- cells. (C) Binding of 2G12 and DC-SIGN to uncleaved JR-FL SOSIP.R6-IZ-D7324 gp140 trimers. (D) Inhibition of DC-SIGN binding to LAI, JR-FL and KNH1144 gp120 and JR-FL SOSIP.R6-IZ-D7324 gp140 by mannan or EGTA. (E) Binding of cleaved KNH1144 SOSIP.R6 MPER gp140 to 2G12 and DC-SIGN, analyzed by immunoprecipitation.