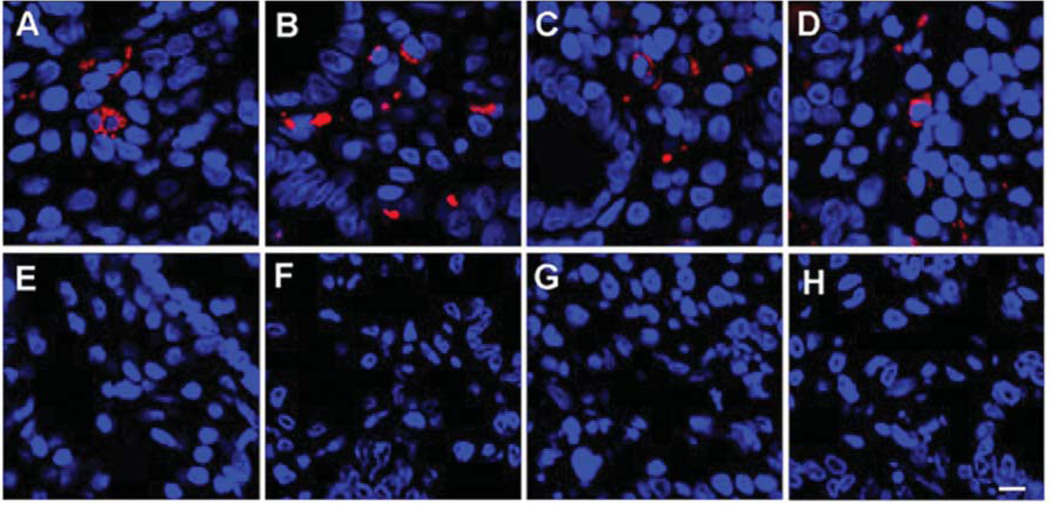
Figure 1.
Immunoreactivity to monoclonal (mAb) and polyclonal (pAb) antibodies against human endogenous retrovirus (HERV) in a duodenal biopsy of representative individuals. A: Immunoreactivity to antiHERVK Gag IgG1 mAb (Dylight594 donkey antimouse IgG secondary) in a duodenal biopsy of an ME case. B: Immunoreactivity to anti-HERVK18.1 Env IgG pAb (Dylight594 donkey anti-mouse IgG secondary) in a duodenal biopsy of an ME case. C: Immunoreactivity to antiHERVFRD Env IgG pAb (rhodamine goat antirabbit IgG secondary in a duodenal biopsy of an ME case. D: Immunoreactivity to antiHERVR Env (rhodamine goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary) in a duodenal biopsy of an ME case. E: Immunoreactivity to antiHERV-K Gag IgG1 mAb (Dylight594 donkey anti-mouse IgG secondary) in a duodenal biopsy of a control. F: Immunoreactivity to antiHERVK18.1 Env IgG pAb (Dylight594 donkey antimouse IgG secondary) in a duodenal biopsy of a control. G: Immunoreactivity to antiHERVFRD Env IgG pAb (rhodamine goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary) in a duodenal biopsy of a control. H: Immunoreactivity to antiHERVR Env (rhodamine goat antirabbit IgG secondary) in a duodenal biopsy of a control subject. (Bar represents 20 µm). TOPO3 was used to indicate nucleus localization in all images.