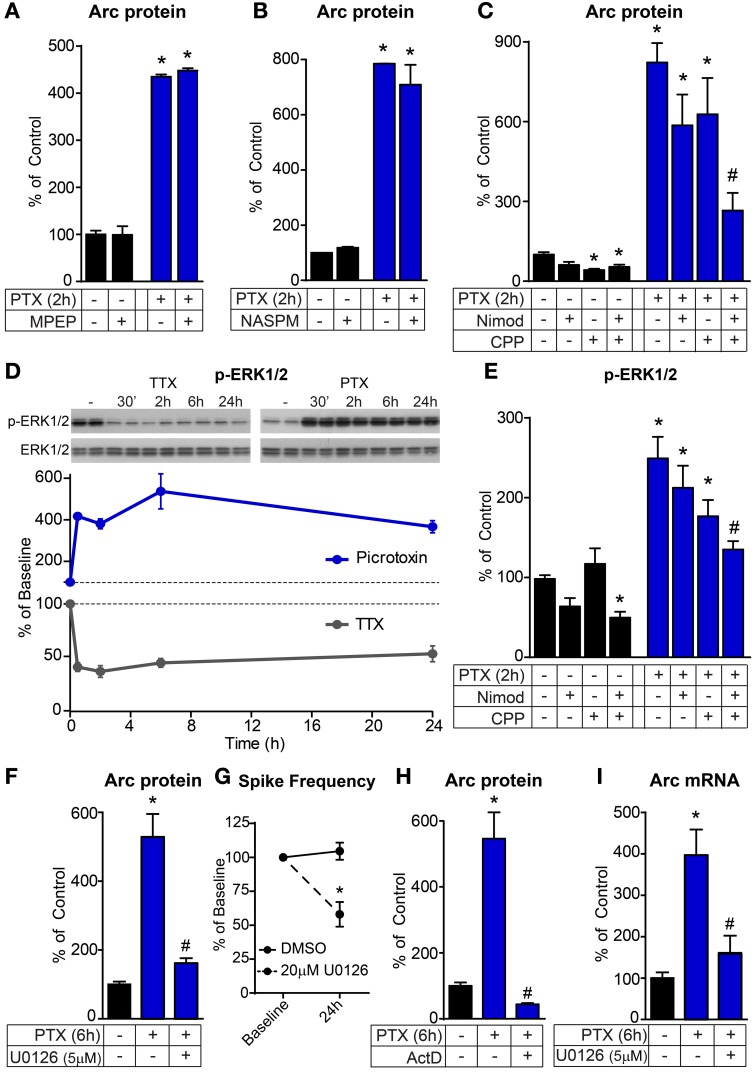
Figure 3.
The activity-dependent induction of Arc requires ERK1/2-dependent transcription. (A–C) Bar graphs displaying western blot data of Arc protein normalized to GAPDH loading control. Hippocampal cultures were treated for 2 h with 50 μM picrotoxin (PTX) and pre-incubated for 30 min with either 4 μM MPEP (A), 10 μM NASPM (B), 5 μM nimodipine (Nimod) and/or 10 μM CPP (C). (D) Top: representative western blots of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2, Thr202/Tyr204) normalized to total ERK1/2 protein following treatment with TTX (left) or picrotoxin (PTX, right) for the indicated times in hours. Bottom: average p-ERK1/2 levels in neurons treated with picrotoxin (blue) or TTX (gray) for the indicated times. Dotted lines at 100% indicate baseline levels. (E) Western blot data of p-ERK1/2 normalized to total ERK1/2 following 2 hour treatment with nimodipine, CPP, and/or picrotoxin as indicated. (F,H) Western blot data of Arc protein normalized to GAPDH following six hour treatment with picrotoxin with and without 5 μM U0126 (F) or 8 μM actinomycin D (ActD, H). (G) Spike frequency expressed as a percentage of baseline determined by multi-electrode array recordings of pairs of cultures treated with DMSO or 20 μM U0126 for 24 h. (I) Quantitative RT-PCR data of Arc mRNA levels following six hour treatment with picrotoxin with and without 5μM U0126. All data are from 2–3 independent experiments and are represented as mean ± SEM. *Indicates significant difference (p < 0.05) from control baseline level. # Indicates significant difference (p < 0.05) from picrotoxin treated.