Figure 1.
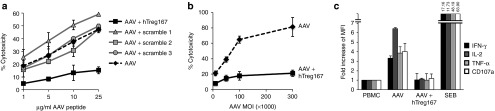
IgG-derived MHC class II epitopes (Tregitopes) mediate suppression of T cell responses in vitro. (a) CTL assay in which target cells were loaded with the AAV-derived MHC I epitope VPQYGYLTL (HLA-B*0702-restricted) at increasing concentrations and then incubated with HLA-matched Teff cells. Effectors were derived from HLA-B*0702 PBMC expanded in vitro against the same MHC I epitope alone (AAV, dashed line), or with hTreg167 (AAV+hTreg167, black line), or with three different scrambled versions of hTreg167 (Scramble 1, Scramble 2, and Scramble 3, grey lines). Teff:target ratio 10:1. Results are expressed as % cytotoxicity compared with a maximum cytotoxicity (cells treated with 10% SDS) after background subtraction. (b) CTL assay in which target cells were transduced with an AAV vector at increasing multiplicity of infections (MOIs) and then incubated with HLA-matched Teff cells restimulated with the AAV capsid MHC I peptide VPQYGYLTL alone (dashed line), or together with hTreg167 (black line). MOI, multiplicity of infection. Teff:target ratio 10:1. (c) Flow cytometry analysis of CD8+ T cell responses to the AAV MHC I epitope VPQYGYLTL. PBMC were restimulated in vitro in the presence of the AAV MHC I peptide VPQYGYLTL alone (AAV) or with hTreg167 (AAV+hTreg167) and then washed and incubated with the VPQYGYLTL peptide and stained for markers of T cell effector functions. Results are expressed as fold increase over non-restimulated PBMC incubated with the MHC I peptide VPQYGYLTL. For the analysis of flow cytometry data, after live/dead exclusion, cells were gated on lymphocytes, CD3+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells were then analyzed for IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α. SEB, Streptococcal enterotoxin B. Experiments shown were repeated at least twice. Error bars represent SEM. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
