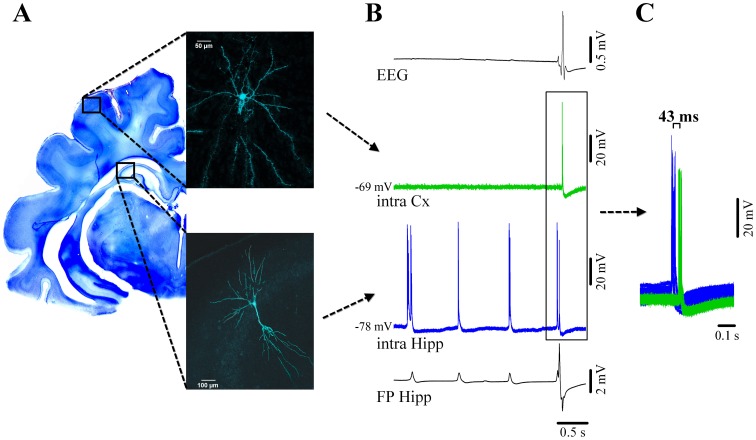
Figure 4. Cortical and hippocampal neuronal activity during νC state.
(A) Neocortical pyramidal neuron from suprasylvian area 5 (above) and simultaneously recorded pyramidal CA3 hippocampal neuron filled with Lucifer Yellow and reconstructed with confocal microscopy. Their respective locations are schematically indicated on a Nissl-stained coronal section of the brain. (B) From top to bottom: simultaneous recording of the EEG, intracellular cortical neuron (green), intracellular hippocampal neuron (blue) and adjacent hippocampal field potential (FP). Both hippocampal traces indicate the presence of two types of activities: delta ripples at about 1 Hz (small amplitude positive potentials in the FP, accompanied by bursts of action potentials in the nearby neuron), and a νC (high amplitude spiky multiphasic potential in the FP, which is paralleled by neuronal discharge). The EEG displays a continuous isoelectric line during hippocampal ripples but displays the νC during which the cortical neuron discharges bursts of action potentials. Delta ripples are not expressed in the neocortex. (C) Time relationship between neuronal discharges for νC events indicating that the hippocampal discharges consistently precede the neocortical ones.