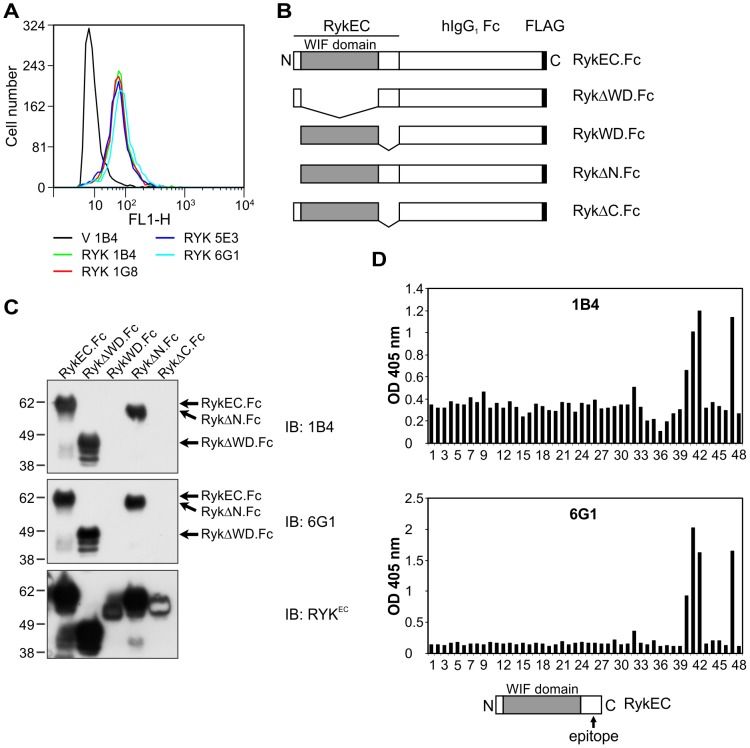
Figure 1. Generation of mouse MAbs to the RYK extracellular region and epitope mapping.
(A) Flow cytometry using purified mouse anti-RYK MAbs 1B4, 1G8, 5E3 and 6G1 on 293-EBNA cells stably expressing pVITRO3-mcs (empty vector control; V) or hRYKFCT (RYK). All antibodies detected RYK in hRYKFCT-transfected but not vector-transfected cells. (B) Schematic of the mouse Ryk fusion proteins used in this study. EC, extracellular region; WD, WIF domain. (C) Western blot analysis of purified mouse Ryk fusion proteins using mouse anti-RYK MAbs 1B4 and 6G1. The pattern of binding was the same for both antibodies. The presence of all the fusion proteins was confirmed by stripping the membrane and reprobing with rabbit anti-RykEC polyclonal antibody. Molecular mass standards are shown at left in kDa. IB, immunoblot. (D) ELISA results using mouse anti-RYK MAbs 1B4 and 6G1 on an immobilized peptide library of the entire human RYK extracellular region. Peptides 3 to 37: RYK WIF domain; peptide 47: FLAG epitope (incubated with mouse anti-FLAG M2 MAb; positive control); well 48: empty (negative control). The MAbs were used at 2 µg/mL. All antibodies bound to the same epitope, in peptides 40−42. The location of the epitope is shown schematically (bottom). Epitopes for the 1G8 and 5E3 antibodies were identical (data not shown). OD, optical density.