Figure 1. UPGMA dendrogram depicting the genetic relatedness of all C. albicans isolates subjected to MLST and ABC genotyping analysis in the present study.
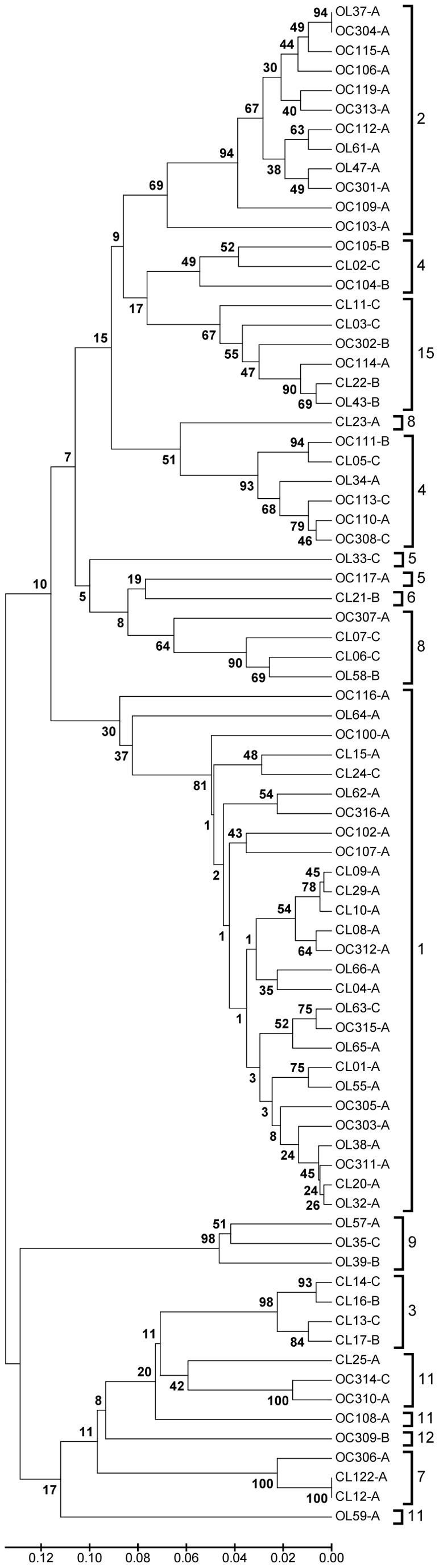
Individual isolates recovered from CL (n = 25) and NCL (n = 19) patients are indicated with the letters CL and OL in the isolate names, respectively. The numeral part of the isolate name refers to the corresponding patient numbers as shown in Table 1, column 1. Isolates recovered from age and sex-matched healthy control patients (n = 34) by oral rinse are indicated using the letters OC in the isolate name. Hyphenated letters A, B or C following each isolate name indicate ABC genotypes. The scale bar indicates p- distance. Distinct MLST clades are indicated by separated square parenthesis to the right of the isolate names and labelled with previously designated clade numbers [17]. Numbers at clade branches indicate bootstrap support levels, based on 1000 replications. Overall, the population analysis based on MLST suggests no clonal enrichment of C. albicans isolates recovered from CL or NCL lesions. Isolates recovered from CL patients are distributed among eight clades, isolates from NCL patients are distributed among eight clades and isolates from healthy carriers are distributed among nine clades, with clade 1 predominating in all three groups.
