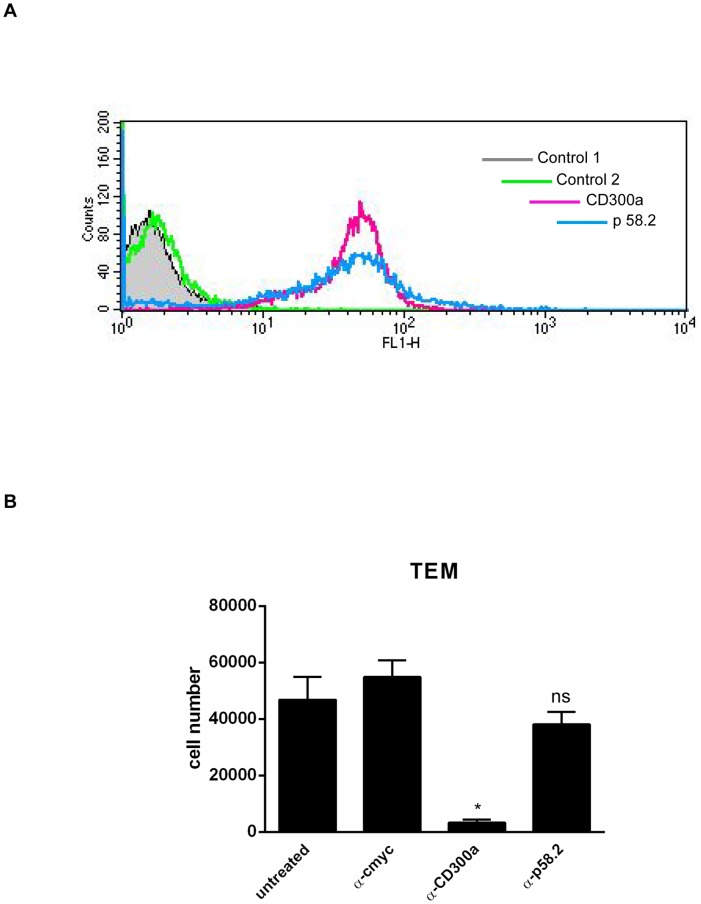
Figure 2. CD300a activation by antibody-engagement on the cell surface of monocytes results in a significant reduction of transendothelial migration.
A. Cell surface expression of CD300a and p58.2 antigens on human monocytes was analysed by FACS using anti-CD300a and anti-p58.2 antibodies. Control cells were incubated without primary and secondary (control 1) or only with secondary antibodies (control 2). B. Freshly isolated human monocytes (2×106) were incubated with mouse monoclonal anti-CD300a (E59.126) or control antibodies (anti-cmyc and anti-p58.2), respectively, and then subjected to transendothelial migration assays in a two-chamber set-up. Migrated cells were collected from the lower chamber and counted using a cell culture analyzer. The number of transmigrated cells is given on the y-axis. Three independent experiments were performed and results are presented as average +/− SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated using student's t-test. * P<0.05.