Figure 5. SHobs Freezing Occurs as Early as 30 min Post-Observer Footshock and Occurs Between Cagemates and Strangers.
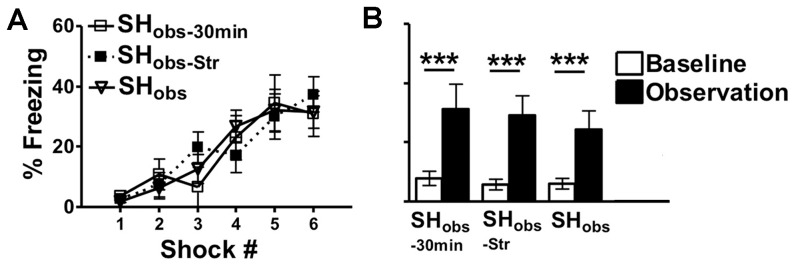
A) On day 1, SHobs, SHobs-Str and SHobs−30 min revealed a significant acquisition of fear learning in context A without differences between groups. B) On day 2, SHobs, SHobs-Str and SHobs−30 min showed similar levels of low baseline freezing and a similar levels of observational freezing. SHobs−30 min = observers that received footshocks in context A, and then witnessed footshocks given to cagemate in context B 30 min later. SHobs-Str = observers that received footshocks in context A on day 1, and then witnessed footshocks given to a non-cagemate in context B on day 2. SHobs = observers that received footshocks in context A, and then witnessed footshocks given to cagemate in context B 24 h later. Data are mean freezing scores +/− S.E.M (n = 8–15 mice per group). (***p<0.001). Within each experimental group there were no differences in the freezing of sexes in context A or context B.
