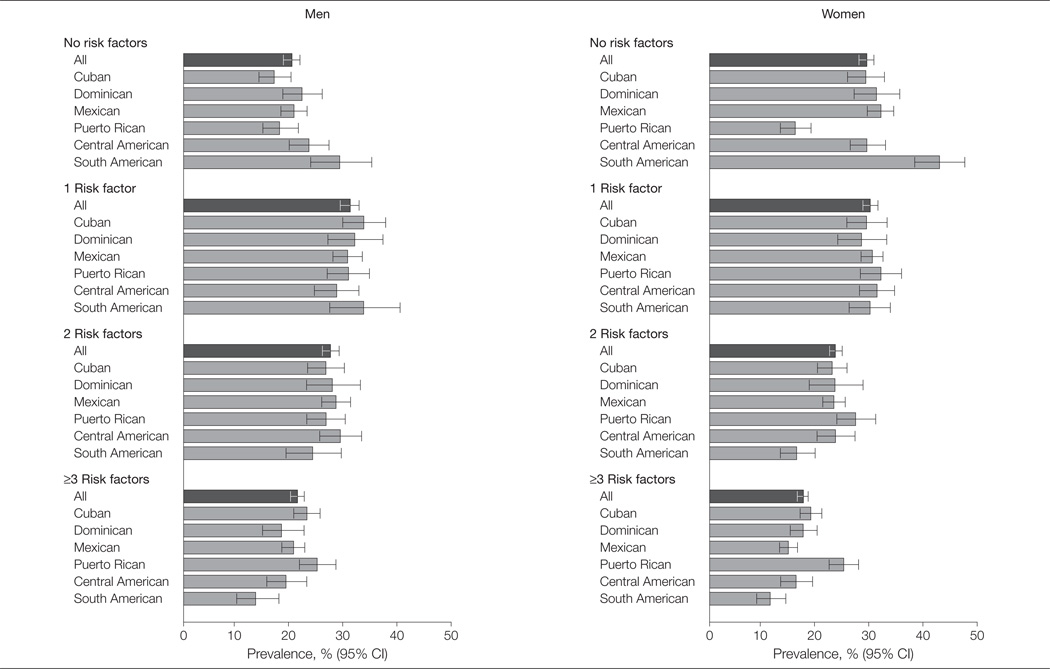
Figure 1. Prevalence of Adverse Cardiovascular Disease Risk Profiles for All Participants and by Hispanic/Latino Group and Sex.
Risk factors were hypercholesterolemia (serum total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL or taking cholesterol-lowering medication), hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive medication), obesity (body mass index ≥30, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared), diabetes mellitus (use of diabetes medication, fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dL, 2-hour-postload plasma glucose ≥200 mg/dL, or hemoglobin A1c ≥6.5%), and smoking (current cigarette smoker). Values were weighted for survey design and nonresponse and adjusted for age. Error bars indicate 95% CI.