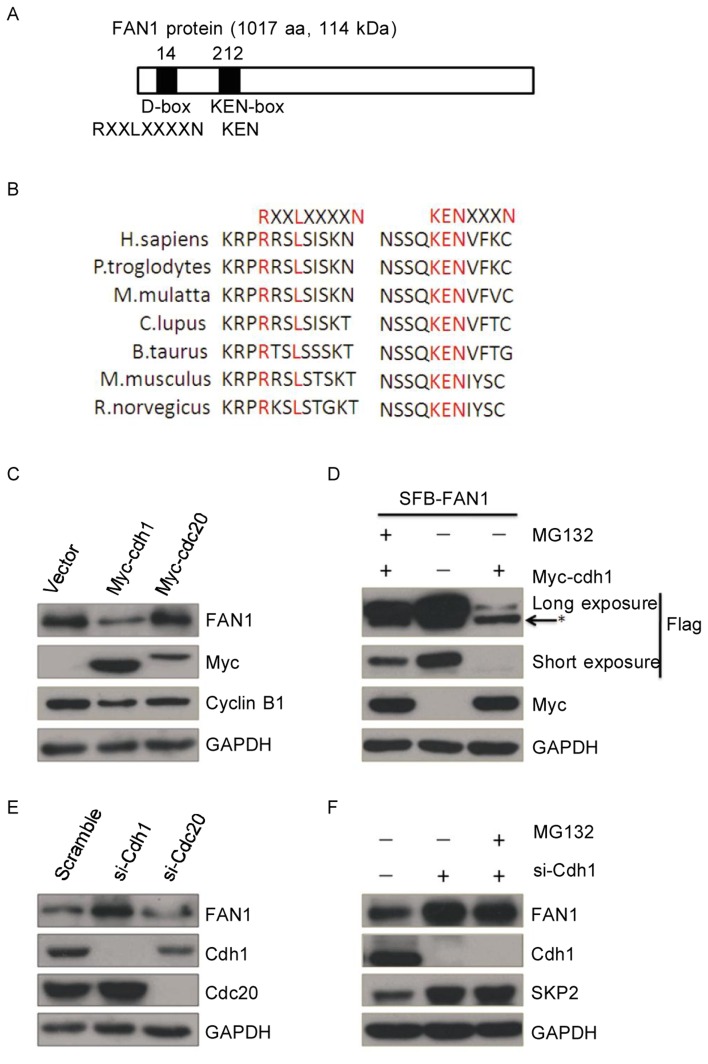
Figure 1. FAN1 is regulated by Cdh1.
A, a schematic presentation of FAN1 (a 1017-aa, 114-kDa protein) denoting the two putative degradation signals, including one D-box (RxxLxxxxN) and one KEN-box. The numbers along the top of this diagram denote the amino acid number at which the consensus sequences start in relation to the start codon. Conserved amino acids are indicated below the bar in bold print, and nonconserved residues are denoted by X. B, a schematic presentation of the KEN-box and D-box of KIAA1018/MTMR15/FAN1 orthologs from different species. The relevant protein identification codes are as follows: Homo sapiens NP_055782.3; Pan Troglodytes XP_510266.2; Macaca mulatta Xp_001109813.1; Canis lupus familiaris XP_856650.1; Bos taurus NP_001158142.1; Mus musculus NP_808561.2; and Rattus norvegicus XP_219706.4. C, U20S cells were transiently transfected with 2 µg of the indicated plasmids for 24 h and then subjected to western blotting. D, U20S cells transiently transfected with 2 µg of the indicated plasmids for 24 h were treated with or without MG132 for 8 h and then were subjected to western blotting. An asterisk (*) indicates a non-specific band. E, U2OS cells were transiently transfected with Cdh1 siRNA, Cdc20 siRNA, or scrambled siRNA for 48 h and then were subjec-ted to western blotting. F, U2OS cells were transiently transfected with Cdh1 siRNA or scrambled siRNA for 48 h, treated with or without MG132 for 8 h, and then subjected to western blotting.