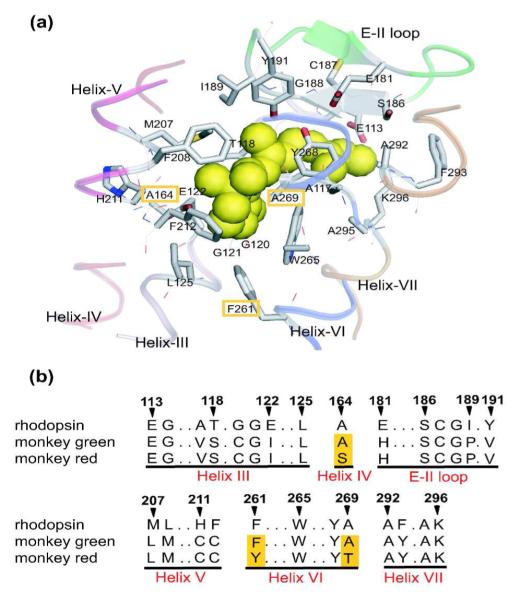
Figure 2.
a) The X-ray crystallographic structure of the chromophore-binding site of bovine rhodopsin (Protein Data Bank entry: 1U19[13]), which is viewed from the helix VI side. The upper and lower regions correspond to the extracellular and cytoplasmic sides, respectively. The retinal chromophore, which is bound to Lys296, is shown by green space-filling model. Side chains of the 27 amino acids around retinal are shown by stick drawings, though some residues behind the retinal are hidden. Ribbon drawings illustrate the secondary structures around the retinal. Corresponding amino acids in monkey green and red pigments are identical except for three amino acids highlighted in orange. b) Partial amino acid sequences of rhodopsin (bovine and monkey), monkey green, and monkey red. The amino acids are identical between bovine and monkey rhodopsins. The three amino acids that differ in monkey green and red are highlighted in orange columns. The residue numbers are based on the bovine rhodopsin sequence. This figure is taken from reference 12.