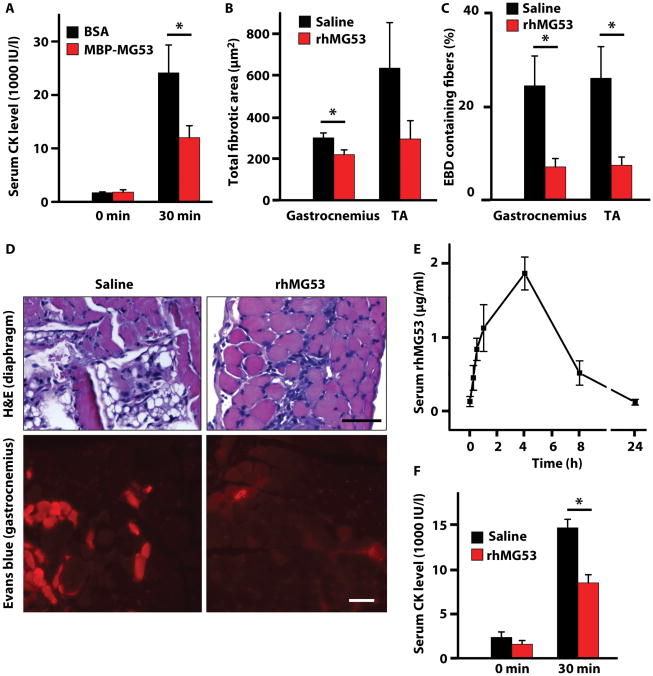
Figure 6. Recombinant MG53 protein therapy reduces pathology in the mdxdystrophic mouse model.
(A) Resting CK levels (pre-running) were measured for 4-week–old mdx mice (n=4 per group) before they were injected intravenously with a single dose of either 4 mg/kg MBP-MG53 or with BSA as a control. These mdx mice were then exercised on a rodent treadmill with downhill running (15°) at 10 m/min for 90 min. CK levels were measured 30 minutes after completion of exercise. Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus control by ANOVA. (B) Four-week–old mdx mice were injected twice daily for 4 days with either 8 mg/kg rhMG53 (n=6) or vehicle control (saline, n=8). Area of fibrosis was measured by ImageJ using hematoxylin & eosin–stained sections of gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior (TA) muscles. Data are means ± SEM, *P < 0.05 by t test. (C) Percentage of Evans blue dye–positive fibers measured using fluorescence microscopy of cryosections from gastrocnemius and TA of mdx mice treated with rhMG53 (n=4) or saline control (n=6). Data are means ± SEM, *P < 0.05 by t test. (D) Representative images of H&E-stained diaphragm muscles and fluorescence microscopy of Evans blue dye in gastrocnemius muscle from mdx mice following 4 days of indicated treatments. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) MG53 in serum over time following subcutaneous (SC) injection of rhMG53 (2 mg/kg). Densitometry was quantified from Western blots from 3 animals. Data are means ± SEM. (F) Following SC injection of rhMG53 (8 mg/kg) or saline vehicle, mdx mice (n=6-8 per group) were subjected to downhill running (15°) at 10 m/min for 90 min. CK levels were measured from serum samples taken before running (0 m) at 30 min after the end of treadmill running (30 m). Data are means ± SEM, *P < 0.05 by t test.