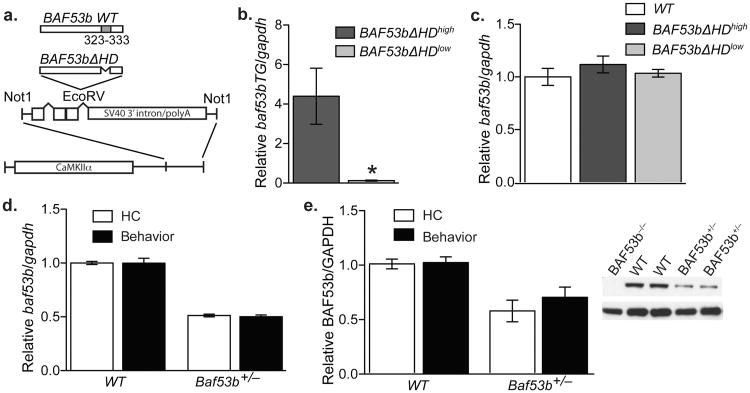
Figure 1.
Characterization of BAF53bΔHD and Baf53b+/− het mice. (a) Wildtype BAF53b is diagramed with hydrophobic domain (HD) shown in grey. In the BAF53bΔHD construct the amino acids 323-333 within the hydrophobic domain were deleted. The BAF53bΔHD mutant sequence was cloned into a separate vector containing intron and exon sequences with splice sites and the SV40 intron and polyadenylation signal, which was then cloned downstream of the 8.5 kb mouse CaMKIIα promoter. This construct was used to generate BAF53bΔHD transgenic mice. (b) Quantitative RT-PCR was performed with transgene specific primers to measure transgene expression in dorsal hippocampus of two independently derived lines of BAF53bΔHD mice. We identified two significantly different lines (Mann-Whitney U (18)=0.00, p<0.0001): a low expressing line (n=10) and a high expressing line (n=10) (2 out of 12 founder lines). (c) Wildtype BAF53b expression in the dorsal hippocampus of BAF53bΔHDhigh (n=10) and BAF53bΔHDlow (n=11) is not significantly different (Kruskal-Wallis H2,33=4.03, p=0.13) between mutant mice and wildtype littermates (n=15). (d) Quantitative RT-PCR shows that wildtype Baf53b expression in the dorsal hippocampus of Baf53b+/− het mice (n=13) is significantly (2-way ANOVA main effect of genotype F1,18=17.87, p<0.001) reduced compared to wildtype littermates (n=8). There was no effect of behavior (F1,18=0.81, p=0.38) or interaction (F1,18=0.40, p=0.53) Mean (± SEM). (e) Western blot analysis shows that BAF53b protein in dorsal hippocampus of Baf53b+/− het mice (n=13) is significantly (2-way ANOVA main effect of genotype F1,17=345.0, p<0.0001) reduced compared to wildtype littermates (n=9). There was no effect of behavior (F1,17=0.05, p=0.82) or interaction (F1,17=0.03, p=0.85).