Fig. 7.
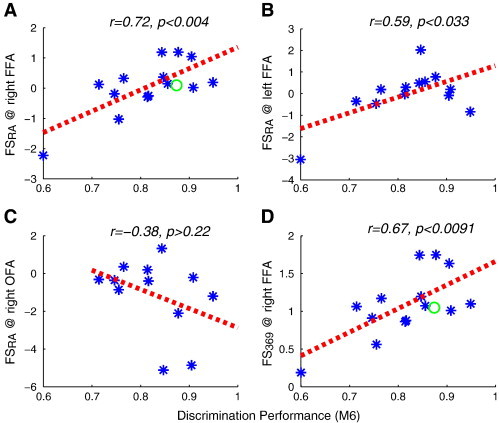
Neural selectivity as estimated with fMRI-RA correlates with face discrimination ability. (A) Mean fMRI responses in the FFA during the fMRI-RA scans revealed only a weak release from adaptation for small shape differences, suggesting a reduced selectivity of face neurons in the FFA in autism. Correlation of behavioral face discrimination performance in the M6 condition and face selectivity FSRA revealed a significant correlation in the right FFA (B) and left FFA (C), but not in the right OFA and other brain regions (see text, not shown). Another index of face selectivity based on activity in the fMRI-RA experiment, FS369, likewise showed strong correlation with behavioral face discrimination ability (D). Green circles in (B) and (D) indicates the average data from adults with typical face perception (Jiang et al., 2006). Dashed lines show the respective regression lines. Error bars show within-subject SEM.
