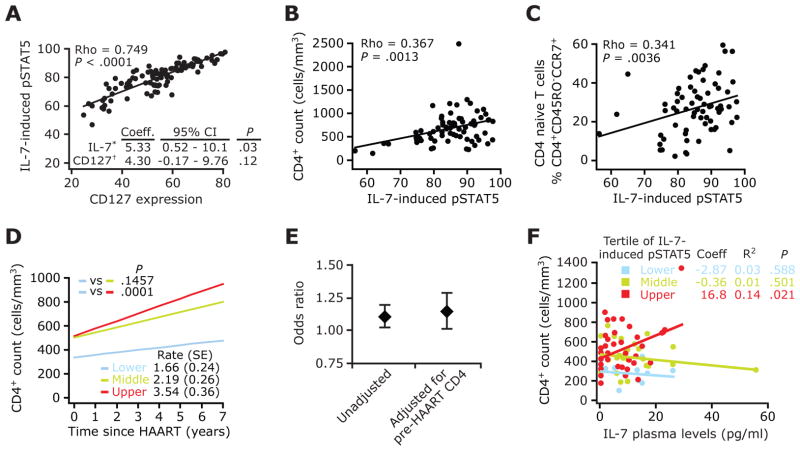
Figure 3.
Responsiveness of T cells to interleukin (IL)-7 is associated with prevailing CD4+ T cell counts during HAART and modulates the influence of plasma IL-7 on immune recovery. A, Scatterplots depicting pairwise correlations between IL-7 responsiveness and CD127 expression in all HIV-positive subjects. Inset, A multivariate linear regression model in which the CD4+ T cell count was the outcome variable and levels of IL-7-induced phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (pSTAT5) (IL-7*) and CD127 (CD127†) were the predictors. Coeff., regression coefficient; CI, confidence interval. Data are derived from 102 HIV-positive subjects. B and C, Scatterplots show the correlation between IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels and total (B) and naive (C) CD4+ T cell counts in subjects with viral load (VL) suppression. A–C, Numbers in the upper left denote Spearman’s ρ coefficient and significance. Data in panels B and C are for 74 and 69 subjects with VL suppression, respectively. D, CD4+ T cell trajectories from the time of initiation of HAART in subjects with VL suppression, according to the upper, middle, and lower tertiles of IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels. The overall monthly rate of CD4+ T cell gains (± standard error [SE]), as estimated by linear generalized estimating equations, is shown at the bottom right. P values denote differences in rates of increases in CD4+ T cell counts between tertiles of IL-7-induced pSTAT5, with the lower tertile (blue) used as the reference group. The number of subjects and the number of CD4+ T cell count measurements (shown in parentheses) in the lower, middle, and upper tertiles of IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels were 13 (186), 27 (418), and 34 (541), respectively. E, Results of nested logistic regression analyses in which the likelihood of a complete immunologic response associated with responsiveness of T cells to IL-7 (IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels were used as a continuous variable) was computed before and after adjustment for the pre-HAART CD4+ T cell count. Diamonds and error bars denote the odds ratio and 95% CI, respectively, of having a complete immunologic response. Data are derived from 66 subjects with VL suppression. F, Association between plasma IL-7 levels and prevailing CD4+ T cell counts within each tertile of IL-7-induced pSTAT5. IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels were categorized into tertiles, and the correlation between IL-7 levels and CD4+ T cell counts among subjects categorized as belonging in these tertiles is shown. Linear regression was used to predict the mean CD4+ T cell count based on endogenous plasma IL-7 levels in subjects with VL suppression. Numbers correspond to the Spearman ρ coefficient (Coeff.) and the P value for each tertile of IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels. R2 indicates the amount of variance in CD4+ T cell count that is explained by plasma IL-7 levels within each tertile of IL-7 responsiveness. Numbers of subjects in the lower, middle, and upper tertiles of IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels were 13, 27, and 34, respectively.