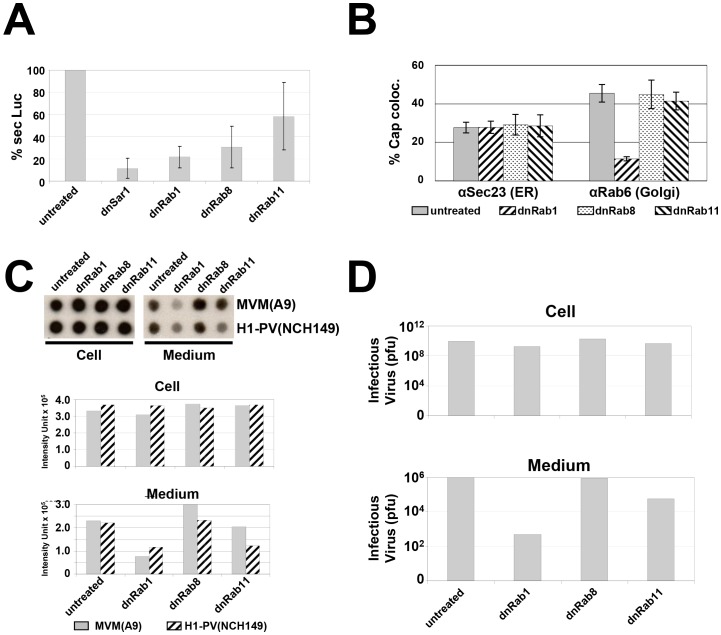
Figure 3. Cytoplasmic transport of progeny PV virions.
(A) GLuc secretion through ER and golgi. A9 cells were transfected with pCMV-GLUC and transduced with rAAV:P38-dnRab1 (expressing dominant-negative rab1 (dnRab1)), rAAV:P38-dnRab8 (dnRab8) or rAAV:P38-dnRab11 (dnRab11), respectively, together with rAAV:P4-Transactivator. The amount of secreted GLuc was measured in the medium 72 h post transduction. Inhibition of GLuc secretion was determined in four independent experiments and mean values are displayed. rAAV:P38-dnSar1 served as a positive control. (B–D) A9 cells were infected with MVMp (30 pfu/cell), NCH149 cells with hgH1-PV (30 pfu/cells). When indicated, rab-protein functioning was inhibited by over-expression of the dominant-negative rab-variant (dnRab1, dnRab8, dnRab11), transduced by rAAV 24 h prior to parvovirus infection. Treated cells were processed at 24 h p.i. (B) Virus-neutralizing antibodies were added from 4 h p.i. on. Cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained for MVM capsids together with either Sec23 (ER) or Rab6 (golgi), respectively, to monitor transport through these compartments ( Fig. S3). Colocalization was quantified by Image J analyzing 10 infected cells from three individual experiments. Grey columns: A9 untreated cells (untreated); hatched columns: A9 expressing dnRab1; dotted columns: A9 cells expressing dnRab8; back-hatched columns: A9 cells expressing dnRab11. (C, D) Viral particles released into the medium. Medium and cell-associated virions were collected separately and quantified (C) by dot-blot hybridization analyses for the DNA content and (D) by standard plaque assays for infectious particles. Grey columns: MVM virion DNA; hatched columns H1-PV virion DNA.