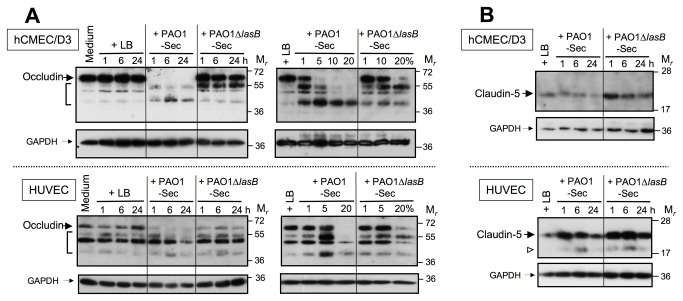
Figure 7. The LasB-containing secretome alters tight junction proteins in endothelial cells in culture.
(A) Confluent EC cultures were exposed for 1 to 24 h to low FCS culture medium alone or with 10% of either LB, PAO1-Sec, or PAO1∆lasB-Sec (left-hand panels), or for 24 h to culture medium with LB (20%) or with the bacterial secretomes in the range of 1 to 20% (right-hand panels). Total proteins extracted from residual adherent cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/IB under reducing conditions (2 to 5 μg per well) for detection of cell-associated occludin using an anti-occludin pAb (0.5 μg/mL; upper panels), then membranes were reprobed with the anti-GAPDH mAb (lower panels). Located on the left-hand side are full-length occludin (large black arrows), GAPDH (small black arrows), and shorter species of occludin seen with bacterial secretomes (brackets in upper panels). (B) Confluent EC cultures were exposed for 1 to 24 h to low FCS culture medium with 10% of either LB, PAO1-Sec, or PAO1∆lasB-Sec, and SDS-PAGE/IB was used as above to detect cell-associated claudin-5 using an anti-claudin-5 pAb (1.25 μg/mL). Full-length claudin-5 is indicated by large black arrows, and GAPDH by small black arrows. Occasionally a previously described truncated species of claudin-5 of Mr ≈ 17 kDa [52] was detected in HUVECs, and this could be seen with either PAO1-Sec or PAO1∆lasB-Sec (open arrowhead in upper panels).