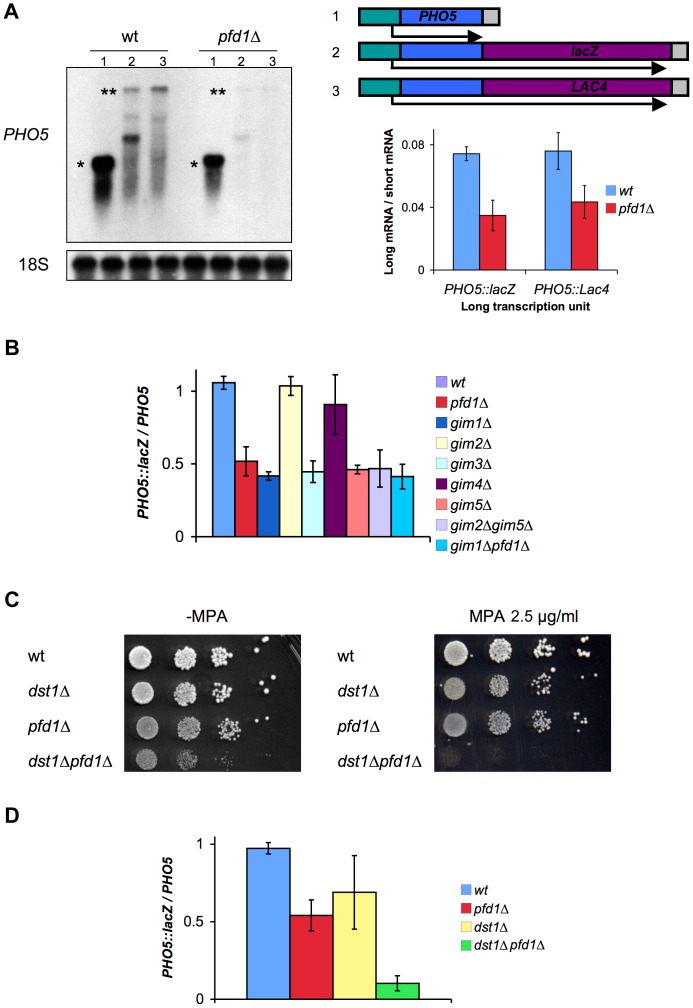
Figure 2. Prefoldin mutants exhibit transcriptional phenotypes and synthetic interactions with TFIIS.
A. pfd1Δ was impaired in the accumulation of 4.5 kb long mRNAs (**), but behaved as the wild type when expressing a 1.5 kb mRNA (*) driven by the same promoter. A single short transcription units (1) was utilized, but two different long transcription units were tested in order to exclude sequence-specific defects: GAL1pr-PHO5::lacZ (2) and GAL1pr-PHO5::LAC4 (3). A significant Northern experiment is shown on the left. The average ratios calculated dividing the signals of the long transcript by the signal of the short transcript are shown on the right. Values correspond to the mean and the standard deviation of three biological replicates. B. Four out of six prefoldin mutants, lacking the yeast prefoldin complex subunits, exhibited significantly lower GLAM ratios than the wild type. The GLAM ratios of double mutants were no lower than single ones. GLAM ratios were calculated dividing the acid phosphatase activity of cells expressing GAL1pr-PHO5::lacZ by the activity of cells of the same strain expressing GAL1pr-PHO5. Values correspond to the mean and the standard deviation of three biological replicates. C. The pfd1Δ dst1Δ double mutant exhibited hypersensitivity to 2.5 µg/ml mycophenolyc acid. Ten-fold serial dilutions were used for the drop assay. D. The pfd1Δ dst1Δ double mutant showed synergistically lower GLAM ratios, as compared to the corresponding single mutants. The GLAM ratios in B and D were calculated after measuring the acid phosphatase activity encoded in the GLAM transcription units, and were normalized to the wild-type value to facilitate comparisons. Values correspond to the mean and the standard deviation of three biological replicates.