Figure 6. ParB is essential in M. xanthus.
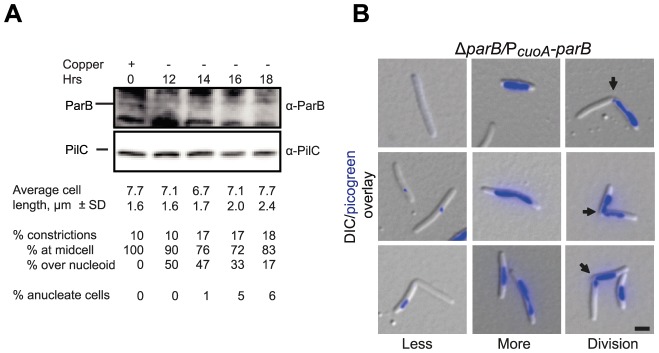
(A) Depletion of ParB. Upper panel, immunoblot analysis of the level of ParB during ParB depletion in SA4269 (ΔparB/PcuoA-parB). Cells were transferred to copper-free medium at t = 0 hrs. The two upper panels show the levels of ParB and PilC during ParB depletion. PilC is involved in type IV pili function [78] and is used as a loading control. Average cell length ± SD, % of cells with constrictions, and of those % of constrictions at midcell and/or over the nucleoid, and % of anucleate cells (n = 100 at each timepoint) are indicated. Cells had a doubling time of 5.5 h in the presence of CuSO4 and in the absence of CuSO4 until 16 hrs. (B) Depletion of ParB causes chromosome segregation and cell division defects. Left panel, anucleate cells or cells with only low levels of DNA stain (blue) (Less). Middle panel, cells with unusually bright DNA stains (More). Right panel, cells with constrictions (arrows) at the edge of chromosomes or over the chromosomes (Division). Images were taken at t = 18 h. Scale bar, 2 µm.
