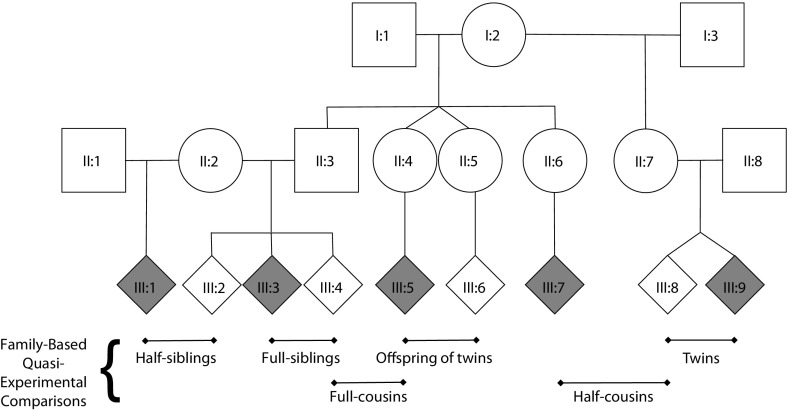
FIGURE 1—
Schematic of extended family pedigree with examples of several family-based, quasi-experimental comparisons.
Note. I = first generation; II = second generation; III = third generation. Squares represent males. Circles represent females. Diamonds represent either males or females. Horizontal lines represent mating and sibling relationships. Vertical lines represent parent-child relationships. Inverted Vs represent twin pairs. Shaded diamonds represent individuals exposed to a risk factor (e.g., maternal smoking during pregnancy). Examples of differentially exposed siblings are presented, including half-siblings (III:1 and III:2, who share 25% of their genes); full-siblings (III:3 and III:4, who share 50% of their genes); and twins (III:8 and III:9, either fraternal twins, who share 50% of their genes, or identical twins, who share 100% of their genes). Differentially exposed cousins are also presented, including half-cousins (III:7 and III:8, who share 6.25% of their genetic factors); full-cousins (III:4 and III:5, who share 12.5% of their genetic factors); and offspring of twins (III:5 and III:6). If the twins (II:4 and II:5) are fraternal, their offspring (III:5 and III:6) would share 12.5% of their genetic factors. If the twins (II:4 and II:5) are identical, their offspring (III:5 and III:6) would share 25% of their genetic factors.