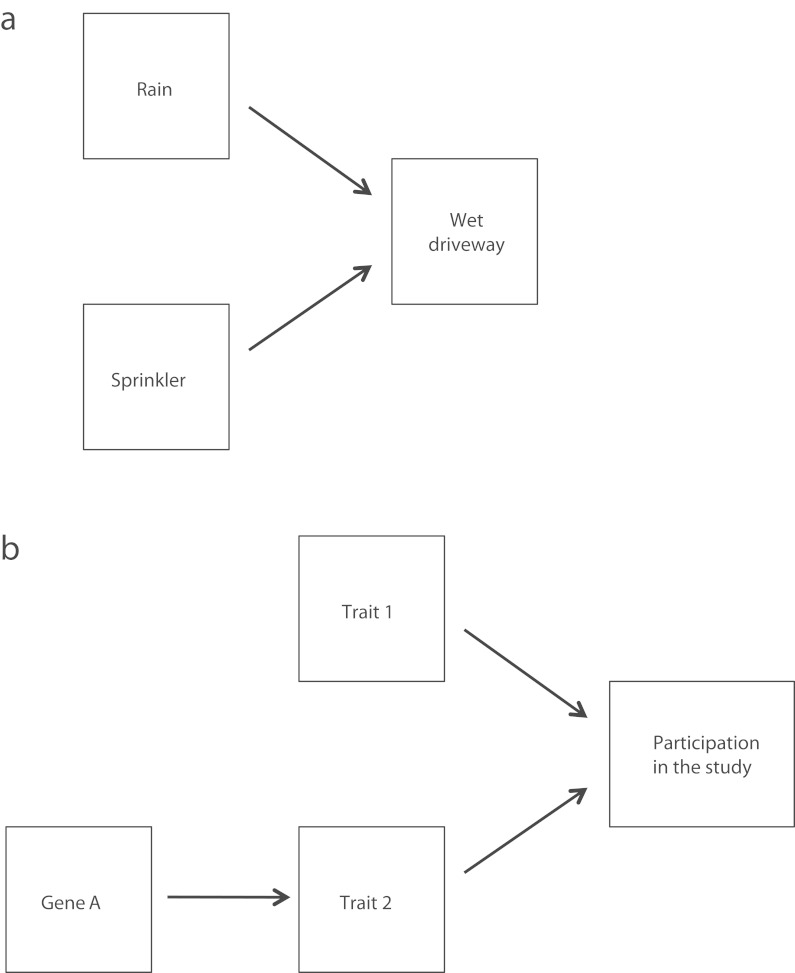
FIGURE 2—
Examples of directed acyclic graphs containing a “collider” (the common effect of 2 or more causes) for (a) 2 uncorrelated causes of a wet driveway that can incorrectly appear to be correlated and (b) situation in which a gene is associated with a trait that is itself a cause of participation in the study.
Note. Conditioning on a collider alters the apparent covariation among the causes; for example, 2 independent causes that are uncorrelated when all observations are considered can appear to be negatively correlated when we consider only those observations where the collider assumes a certain value.
Source. Pearl.42