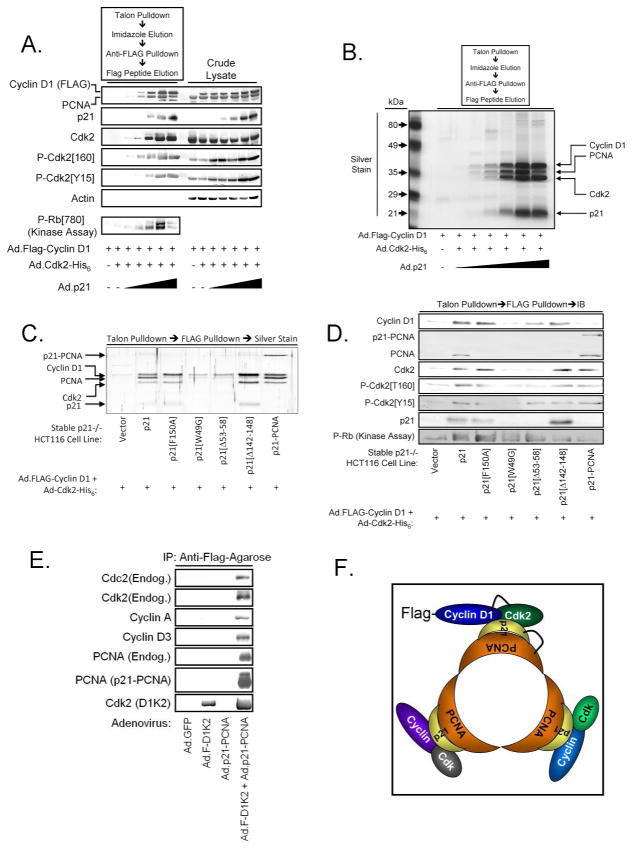
Figure 1.
p21 promotes D1/K2 complex assembly. (A) Immunoblot analysis of crude lysates and affinity purified D1/K2 complexes from p21−/− HCT116 cells infected with adenoviruses encoding Cyclin D1, Cdk2, and increasing amounts of p21. (B) Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel of affinity purified D1/K2 complexes from p21−/− HCT116 cells infected with adenoviruses encoding Cyclin D1, Cdk2, and increasing amounts of p21. (C) Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel of affinity purified D1/K2 complexes from p21−/− HCT116 cells infected with adenoviruses encoding Cyclin D1, Cdk2, and the indicated p21 constructs. (D) Immunoblot analysis of affinity purified D1/K2 complexes from p21−/− HCT116 cells infected with adenoviruses encoding Cyclin D1, Cdk2, and the indicated p21 constructs. (E) Immunoblot analysis of affinity purified Cyclin D1 complexes from p21−/− HCT116 cells infected with adenoviruses encoding the indicated proteins. (F) Model of trimeric p21/PCNA complexes containing multiple Cyclin/Cdk complexes.