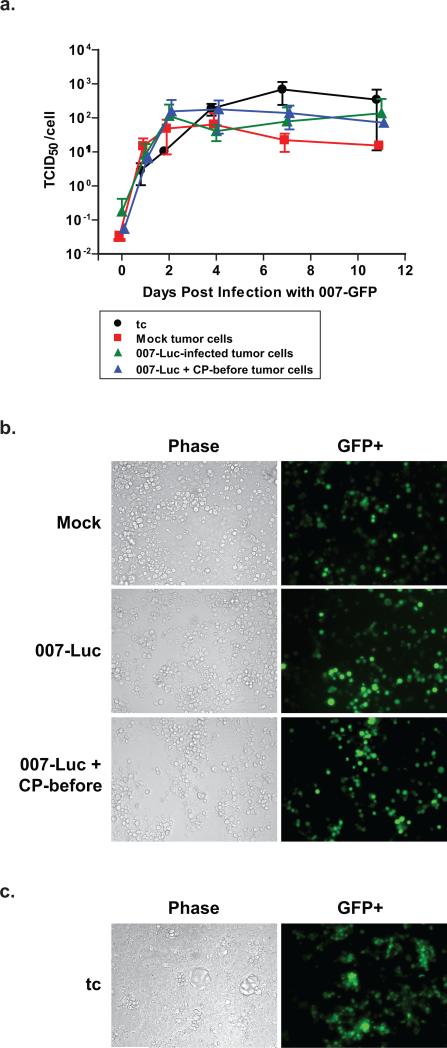
Figure 6. Cells from excised HaK tumors are not resistant to 007-GFP infection in culture.
Three hamsters from the mock, 007-Luc, and 007-Luc + CP-before groups from the experiment in Fig. 4 were selected at random. The tumors from each group were excised and homogenized into single cell suspensions by digestion in trypsin/EDTA for 30 min. 5×104 cells were plated per well in a 12-well plate. Three samples from HaK tissue culture cells were used as well (designated as tc). (a) Single step growth curve. Cells were infected 2 days after isolation with 007-GFP (50 PFU/cell) and then washed with DMEM 5%FBS. At each time point, one 12-well plate with all 12 samples was frozen away. A TCID50 assay was performed. Graphs represent virus yield produced per cell. (P>0.100 between each group on every day). GFP expression in (b) ex vivo tumor cells and (c) tissue culture cells. Images were taken of the tumor cells to determine the presence of GFP+ cells. Images above are representatives of each group, taken 4 days post infection. The number of cells per well at time of infection were as follows: Mock, 1.8×105; 007-Luc, 1.8×105; 007-Luc + CP-before, 1.1×105; tc, 4.4×105.