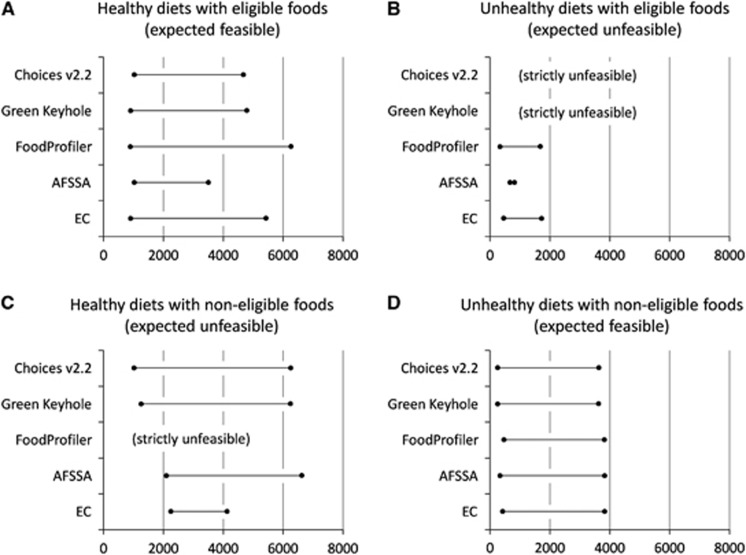
Figure 1.
Energy range, in kcal, to design healthy/unhealthy diets with eligible/non-eligible foods. Test A assesses whether it is feasible to design healthy diets with eligible foods (it is expected to be feasible). Test B assesses whether it is feasible to design unhealthy diets with eligible foods (it is expected to be unfeasible). Test C assesses whether it is feasible to design healthy diets with non-eligible foods (it is expected to be unfeasible). Test D assesses whether it is feasible to design unhealthy diets with non-eligible foods (it is expected to be feasible). ‘Strictly unfeasible' means that no mathematical solution can be found at all. When the energy range includes 2000 kcal, the model is considered feasible. When the energy range excludes 2000 kcal, the model is considered unfeasible.