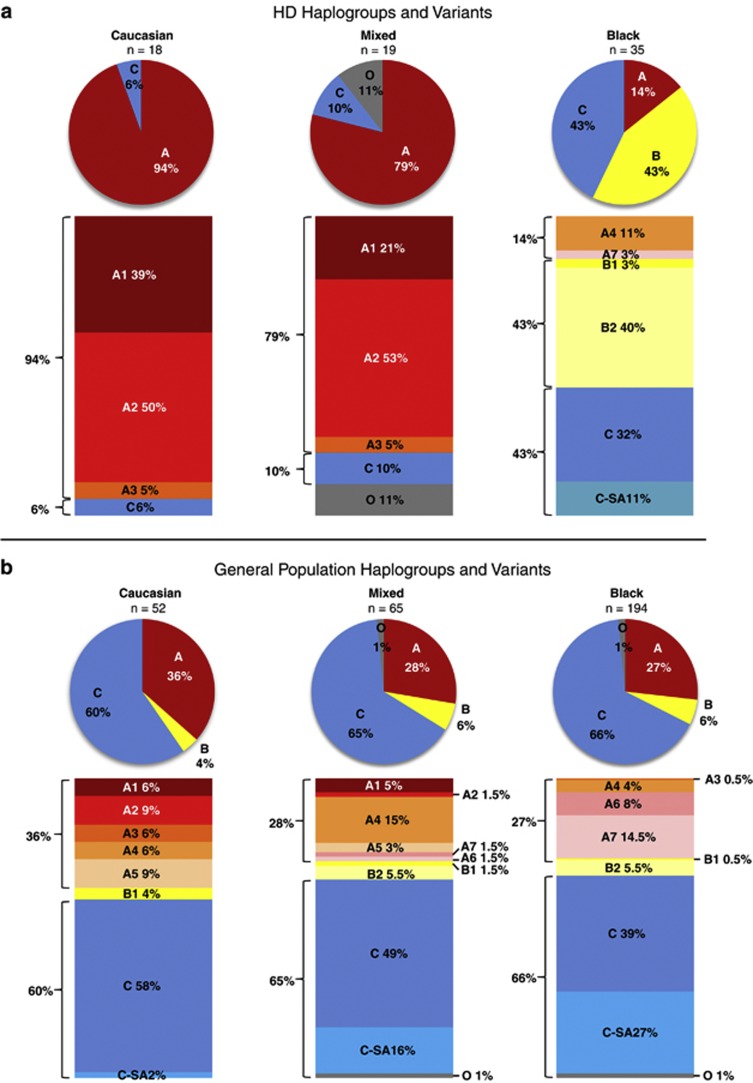
Figure 2.
Haplogroup variants on phased, unrelated alleles from the South African population. (a) HD haplogroups and variants (N=72). HD alleles in the Caucasian subpopulation occur almost exclusively on haplogroup A (94%), predominantly variants A1 and A2 (39% and 50%, respectively). In the mixed subpopulation, the largest proportion of HD alleles also occurs on haplogroup A (79%). Similar to the Caucasian subpopulation, variants A1 and A2 (21% and 53%, respectively) predominate. In the black subpopulation, haplogroup A accounts for only a small proportion of HD alleles (14%), with A1 and A2 absent, whereas the largest proportion occurs on novel variant B2 (40%). (b) General population haplogroups and variants (N=311). In all three subpopulations, the largest proportion of general population alleles occurs on haplogroup C. Haplogroup A in the Caucasian subpopulation accounts for 36% of general population alleles, with variants A1 and A2 present at 6% and 9%, respectively. In the mixed subpopulation 28% of general population alleles occur on haplogroup A, but variant A4 predominates (15%). Haplogroup A also occurs in the black subpopulation (27%) but with a markedly different distribution consisting of A4 and novel variants A6 and A7. A large proportion of all the general population haplotypes in the black subpopulation can be additionally grouped into South African group C-SA (27%), consisting of C haplotypes not previously identified in Caucasian or East Asian populations. Mixed general population haplotypes thus represent an admixture of variants observed in Caucasian and black subpopulations.