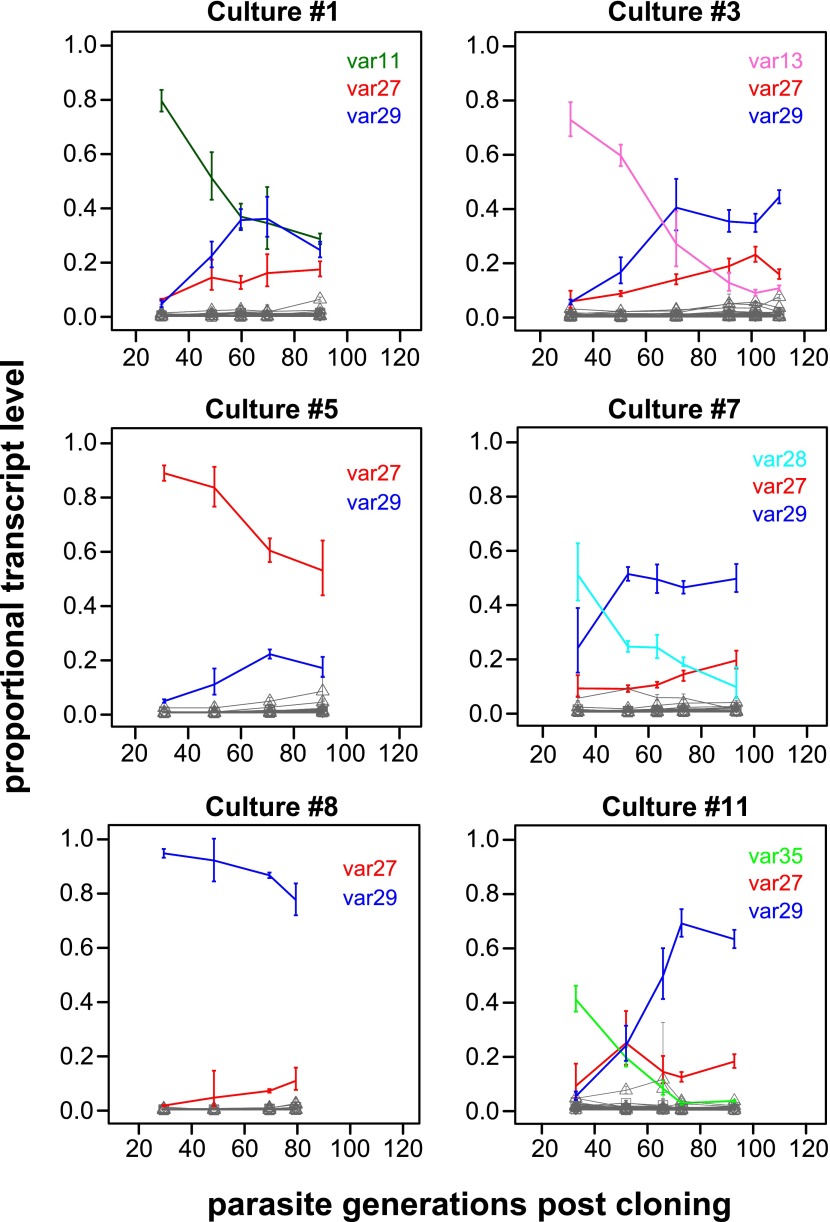
Figure 1. Proportional var transcript levels for six in vitro cultures.
The parasite cultures initially expressed a variety of dominant ‘starter genes’, which switched off at notably different rates. Nevertheless, most cultures converged towards high level transcription of two centrally located genes var27 and var29 (red and blue lines, respectively), whereas most other gene transcripts (grey lines) remained at relatively low levels.