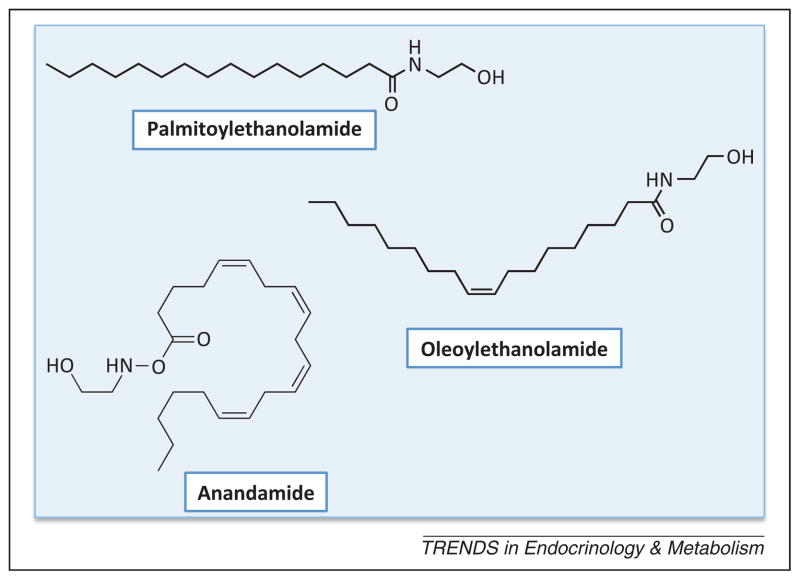
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of three representative fatty acid ethanolamides (FAEs). Palmitoylethanolamide, the first FAE to be discovered, and oleoylethanolamide exert most, albeit not all, of their biological effects by engaging peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α), a ligand-activated transcription factor that can also trigger non-genomic signaling events. Anandamide (arachidonoylethanolamide) is an endogenous agonist for G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors.