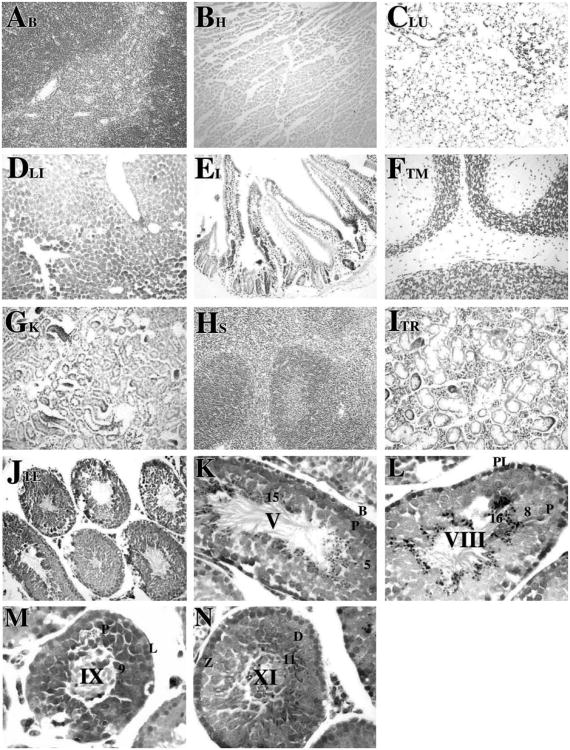
Figure 1.
Tissue-specific and spermatogenic cell-specific expression of β-gal following Cre recombination. Transgenic and non-transgenic control mice were euthanized, perfused with fixatives, and tissues were removed. The tissues were fixed again for 1 h at room temperature in 100 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.3, containing 2% paraformaldehyde, 0.2% glutaraldehyde, 0.1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.2% Nonidet P-40, 5 mM EGTA and 2 mM MgCl2. The tissues were incubated overnight at 30 °C in 100 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.3, 1.3 mM MgCl2, 3 mM K3Fe(CN)6, 3 mM K4Fe(CN)6 and 1 mg/ml 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside (X-gal) as described previously (Langford et al., 1991; Fire, 1992). The tissues were embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 5 μm, and mounted on Superfrost slides (Fisher Scientific, NJ). After X-gal staining, histological sections of brain (A), heart (B), lung (C), liver (D), intestine (E), thymus (F), kidney (G) spleen (H), thyroid (I), and testis (J) were obtained and counterstained with neutral red (Catalogue number N129, Fisher Scientific, NJ) according to standard procedures and viewed on a Nikon photomicroscope under bright-field optics. Photomicrographs were taken using a digital camera (Spot advanced software, Diagnostic Instruments, Inc.). Specific expression of β-galactosidase following Cre recombination was observed only in testis (J). Magnification: ×20. Histological testicular sections from R26RSycp1Cre males were examined at higher magnification (K–N, ×60) to determine cell-specific expression of Cre as detected by X-gal staining. β-gal activity was detected in zygotene spermatocytes at stage XI (N) as very weak signals. The expression was detected continuously from early primary spermatocytes to mid-late pachytene spermatocytes at stage V, VIII (K and L, respectively) to step 1–16 spermatids (K–N). β-gal activity was not detected in Sertoli cells nor in interstitial cells. Abbreviations: B, type B spermatogonia; PL, preleptotene spermatocytes; L, leptotene spermatocytes; Z, zygotene spermatocytes; D, diplotene spermatocytes; P, pachytene spermatocytes; arabic numerals, the step of elongated spermatid; Roman numerals indicated the stage of the seminiferous tubules, staged as described by Russell et al. (1990).