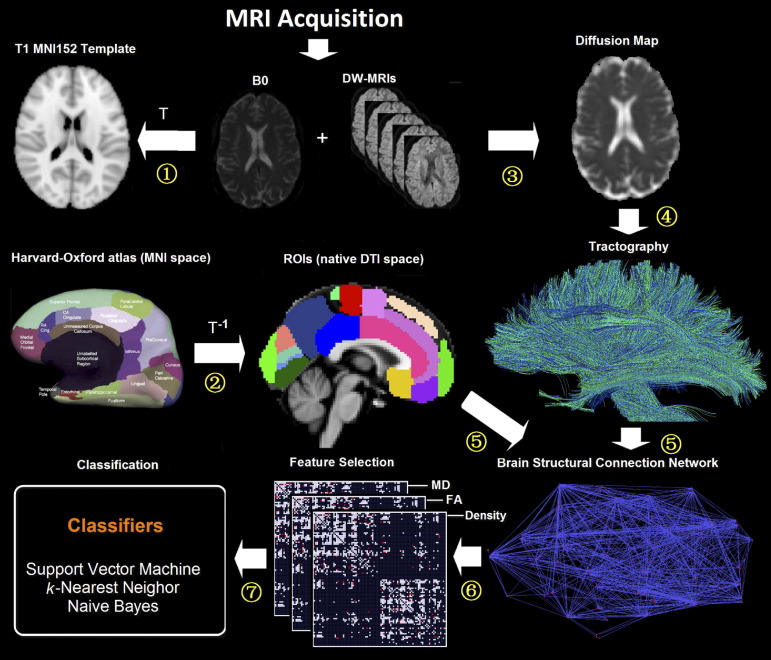
Fig. 1.
Flowchart of DWI image analysis. (1) Individual non-DWI (B0) images were affine-registered to the ICBM 152 template of Montreal Neurological Institute space to obtain the transformation matrix (T) for each participant. (2) The inverse transformation matrix (T−1) was then applied to both Harvard-Oxford brain atlas and (B0) image to generate corresponding cerebral regions in each individual's DWI native space. (3) After preprocessing of DWIs, the local properties of water diffusion (e.g. fractional anisotropy [FA] or mean diffusivity [MD]) were derived from the voxel-wise diffusion tensor model. (4) Whole brain tractography was performed providing an estimate of axonal trajectories across the entire white matter. (5) Individual structural connectivity networks (ISCNs) were constructed by combining the output of both cortical parcellation and diffusion tractography for each individual subject. (6) The most distinctive connections of ISCNs among groups were identified by a feature selection criterion for different attributes of fiber density, FA, and MD. (7) ISCNs of patients with mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer's disease (AD), respectively, and healthy control subjects were classified by three different pattern recognition algorithms.