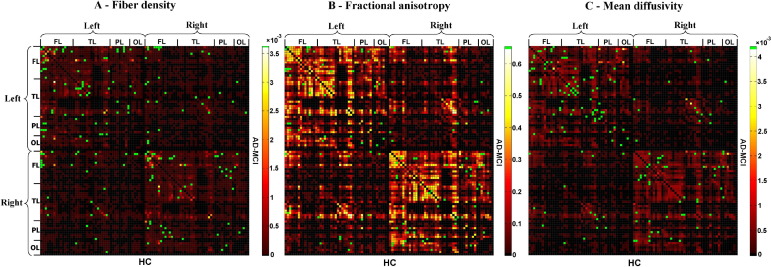
Fig. 3.
Selected connections in ISCNs for the comparison between patients with AD-MCI and healthy control subjects using information gain criterion. The three matrices represent the averaged structural connectivity network based on different attributes: (A) fiber density, (B) fractional anisotropy (FA), and (C) mean diffusivity. Each element of the matrix represents the connection between two cortical regions. In each matrix, the upper triangle matrix indicates the averaged structural connectivity for patients with AD-MCI, and the lower triangle matrix indicates the averaged structural connectivity for healthy control subjects. Black dots indicate that there is no connection for any subject of the group. Red to yellow dots indicate the average of connection attribute across all subjects of the group (yellow indicates higher scores). Note that connection attribute is defined by the mean of, for example, FA values across all voxels of fibers constituting the connection in one subject. Green dots in each matrix indicate the discriminative connections for group comparison selected by information gain criterion in more than 5 rounds of 10-fold cross-validation. FL refers to frontal lobe; TL, temporal lobe; PL, parietal lobe; OL occipital lobe. For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.