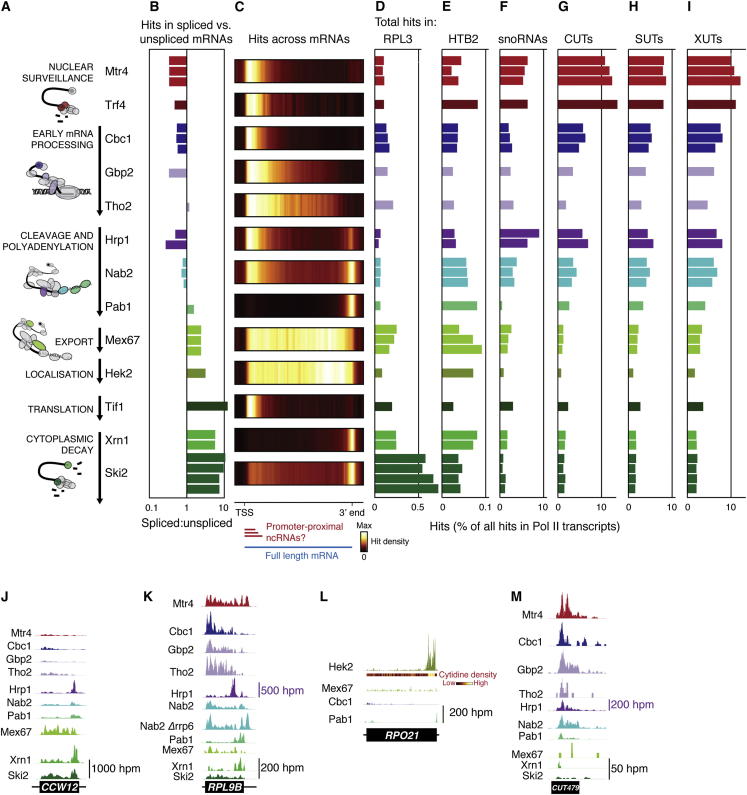
Figure 1.
Transcriptome-wide Analysis of RNP Composition
(A) mRNA maturation and decay factors selected for analysis.
(B) Relative recovery of spliced mRNAs versus unspliced pre-mRNAs bound to the tested proteins, expressed as the ratio of RNA fragments spanning exon-exon:intron-exon junctions.
(C) Average binding distribution of the tested proteins across mRNAs. For each protein, average hit densities were calculated for 120 bins spanning their 1,000 most abundantly bound mRNAs (including 2 × 10 bins for 100 nt 5′ and 3′ flanking regions). 5′-proximal hits can arise from binding to promoter-proximal ncRNAs or to the 5′ end of full-length mRNAs.
(D–I) Total hits for each protein in RPL3 and HTB2 pre-mRNAs, snoRNAs, CUTs, SUTs, and XUTs, as a percentage of all hits in Pol II transcribed RNAs (mRNAs, CUTs, SUTs, snRNAs, and snoRNAs; Table S1).
(J–M) Hit distributions along individual transcripts, at the indicated scales (hits per million hits in Pol II transcribed RNAs). Note the different scale used for Hrp1 data in K and M due to the high level of binding. See also Figure S1 and Table S1.