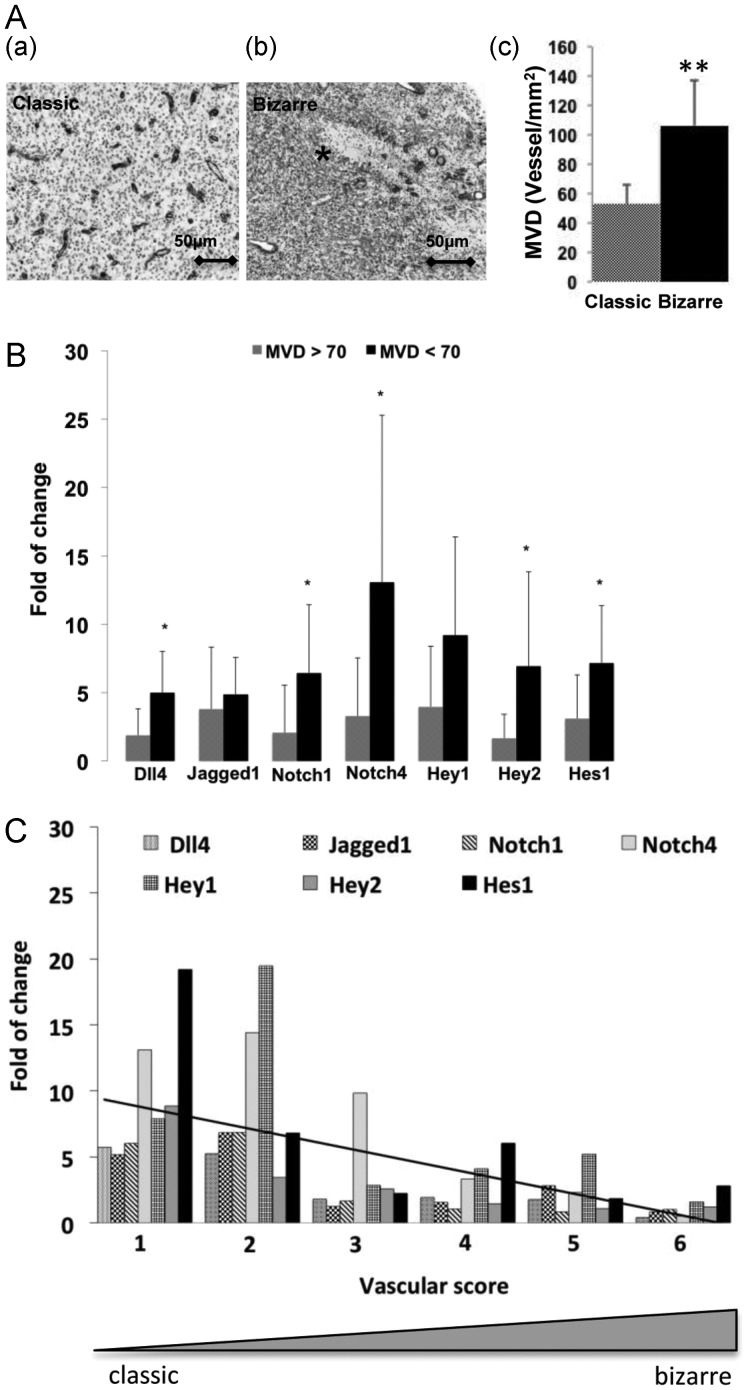
Fig. 3.
Upregulation of Dll4-Notch signaling components was associated with the classic vascular pattern (VP) and lower microvascular density (MVD). The fold of change refers to the relative expression of the individual genes and was calculated based on the expression of the internal reference gene GAPDH and in the relation to the control samples (normal brain). (A) The association of VP with MVD in GBM. VP and MVD were evaluated in GBM sections (n = 26) after staining with laminin, as described in the Methods section. The typical classic (productive) and bizarre (nonproductive) VPs were frequently observed in the infiltrating (a) and necrotic (b, asterisk) areas of GBM tissue, respectively. The classic VP was associated with a lower MVD in GBM (c). **P < .01, compared with the classic vascular pattern. (B) The association of the expression of Dll4-Notch signaling components with MVD. *P < .05, compared with GBMs with a MVD >70 vessels/mm2. (C) The association of the expression of Dll4-Notch signaling components with VP. The tendency from a classic toward a bizarre VP was evaluated in individual GBM samples based on a score ranging from 0 to 6. A smaller score reflected the tendency toward a classic VP and was associated with a greater upregulation of Dll4-Notch signaling components.