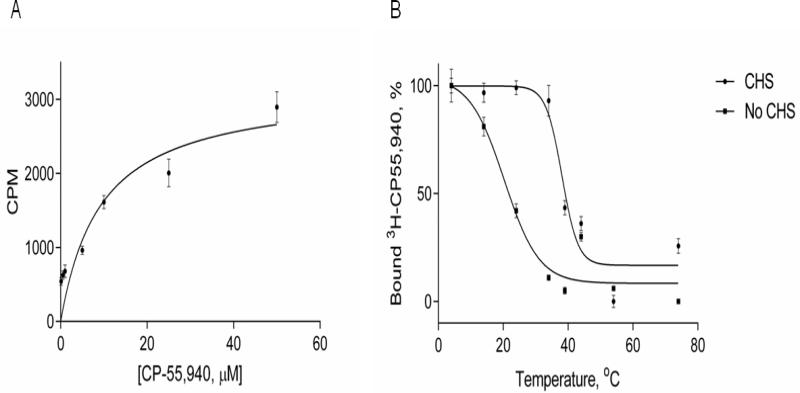
Figure 4. Ligand binding on CB2-255 fusion protein in micelles.
A. Ligand binding on CB2 in detergent micelles. Saturation ligand binding was performed to determine the number of ligand binding sites (Bmax) and affinity (KD) of the interaction between CB2-255 fusion protein and CP-55,940 ligand. Aliquots of CB2-255 fusion protein from crude cell lysate, solubilized in buffer A supplemented with 10 μM CP-55,940 and immobilized onto 1D4-Sepharose resin (50 μL/sample) were washed with solutions of CP-55,940 (0-60 μM) in buffer A, supplemented with [3H]-CP-55,940 and analyzed for ligand binding as described in Material and Methods. Each point represents an average of duplicate measurements. Results of a representative experiment (out of three) are presented.
B. Thermoinactivation of CB2 protein in micelles. The CB2-255 fusion protein from crude lysate in buffer A supplemented with 10 μM CP-55,940 was immobilized on 1D4-Sepharose resin (50 μL/sample) and subjected to a temperature increase from 4 °C to 84 °C at a rate of 1 °C/min. Functional activity of CB2 was analyzed by measuring ligand binding upon addition of [3H] CP-55,940 as described in Materials and Methods. Measurements were performed in duplicate; a representative experiment is shown. Squares- buffer without CHS, circles- buffer with CHS. Results of a representative experiment (three total) are presented.