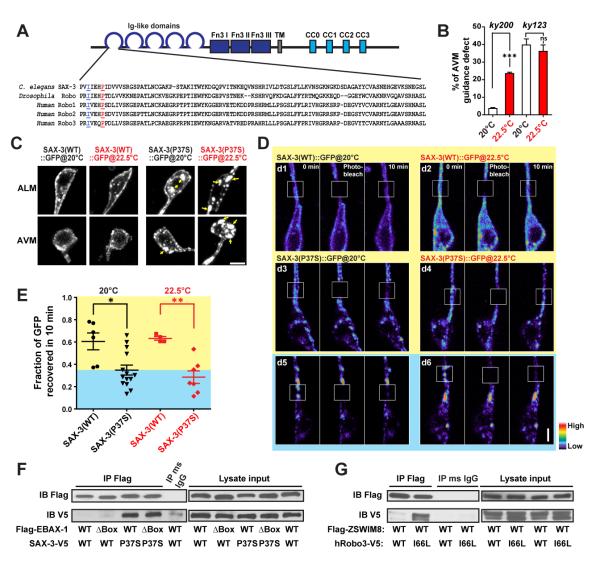
Figure 5. EBAX-1 Preferentially Interacts with a Temperature-Sensitive and Misfolding-Prone Mutant of SAX-3.
(A) Sequence alignment of the Ig1 domain of C. elegans SAX-3, Drosophila Robo and human Robo1, 2 and 3. In the sax-3(ky200) mutant, a conserved Pro37 (marked in red and underlined) is mutated to Ser37. In human Robo3, an I66L mutation (marked in blue and underlined) was found in patients with HGPPS (Jen et al., 2004).
(B) Quantification of AVM guidance defects in the sax-3(ky200) temperature sensitive (ts) and sax-3(ky123) null mutants at permissive (20°C) and restrictive (22.5°C) temperatures. ***p<0.001 relative to the indicated control; t-test.
(C) Subcellular localization of Pmec-7::SAX-3(WT)::GFP and Pmec-7::SAX-3(P37S)::GFP at 20°C and 22.5°C. L1-L2 animals expressing Pmec-7::SAX-3::GFP were imaged for AVM and ALM soma. Yellow arrows indicate cytosolic aggregates of SAX-3(P37S)::GFP. Scale, 2 μm.
(D) FRAP analysis of Pmec-7::SAX-3(WT)::GFP (d1-d2) and Pmec-7::SAX-3(P37S)::GFP (d3-d6) in ALM neurons at the late L1 stage. The fluorescence in regions with strong SAX-3(P37S) aggregates barely recovered after photobleaching (d5-d6), while regions with less aggregation showed a faster recovery rate (d3-d4). The fluorescence intensity is shown as a pseudo-color scale. Scale, 2 μm.
(E) Comparison of the fluorescence recovery rates of SAX-3(WT)::GFP and SAX-3(P37S)::GFP after photobleaching at 20 and 22.5°C. The yellow area indicates the range of SAX-3(WT) samples; the blue area covers mutant samples with slower recovery rates than WT samples. Data shown as scatterplot with means ± SEM. *p<0.05, and **p<0.01; t-test.
(F) Co-immunoprecipitation of Flag-EBAX-1(WT or ΔBox) and SAX-3(WT or P37S)-V5 from HEK293T cell lysates. Immunoprecipitants were subjected to SDS-PAGE separation and immunoblotting (IB) with mouse anti-Flag and mouse anti-V5 antibodies.
(G) Co-immunoprecipitation of Flag-mouse ZSWIM8 (WT) and human Robo3 (WT or I66L)-V5 from HEK293T cell lysates.