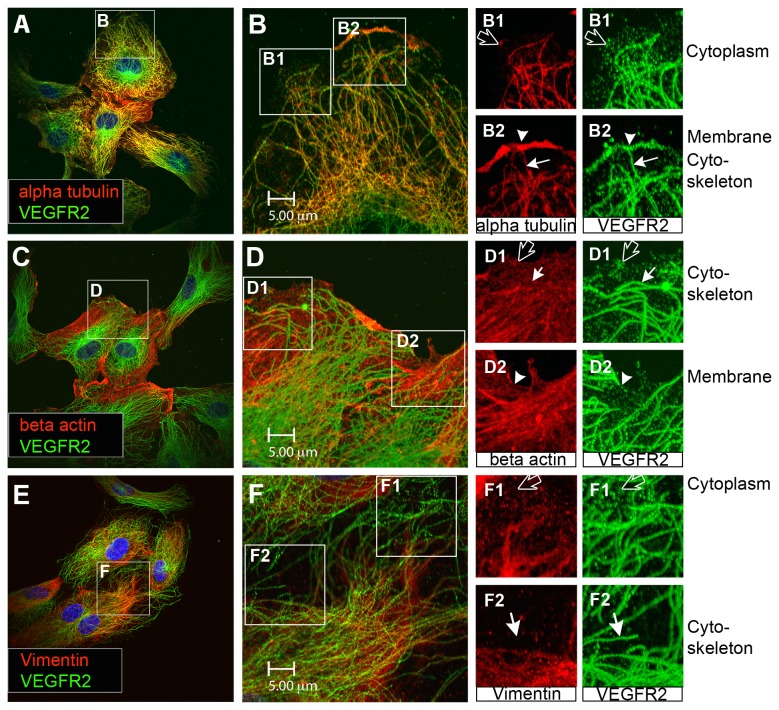
Figure 1. Distinct VEGFR2 pools are present in endothelial cells.
(A) Endothelial cells stained for alpha tubulin (red) and total VEGFR2 (green). (B) Inset from panel A shows cell in more detail. Two insets (B1) and (B2) from panel B separate channels in red and green to more clearly show the distinct pools of VEGFR2 present in endothelial cells. This includes a pool of VEGFR2 on the cell surface (arrowhead), a granular cytoplasmic VEGFR2 pool (black arrow) and a pool of VEGFR2 arranged in fibrous arrays (white arrow). (C) Endothelial cells stained for microfilament beta actin (red) and total VEGFR2 (green). (D) Inset from panel C shows cell in more detail. The insets (D1) and (D2) from panel D separate channels into red and green to demonstrate more clearly distinct pools of VEGFR2 present in endothelial cells. This includes a pool of VEGFR2 on the cell surface (arrowhead, green), a granular cytoplasmic VEGFR2 pool (black arrow) and a pool of VEGFR2 arranged in fibrous arrays (white arrow). (E) Cell stained for intermediate filament Vimentin (red) and total VEGFR2 (green). (F) Inset from panel E shows cell in more detail. Insets (F1) and (F2) taken from panel F separate channels in green and red to show more clearly the distinct pools of VEGFR2 present in endothelial cells. This includes a granular cytoplasmic VEGFR2 pool (black arrow) and a pool of VEGFR2 arranged in fibrous arrays (white arrow). All displayed images are single focal planes.