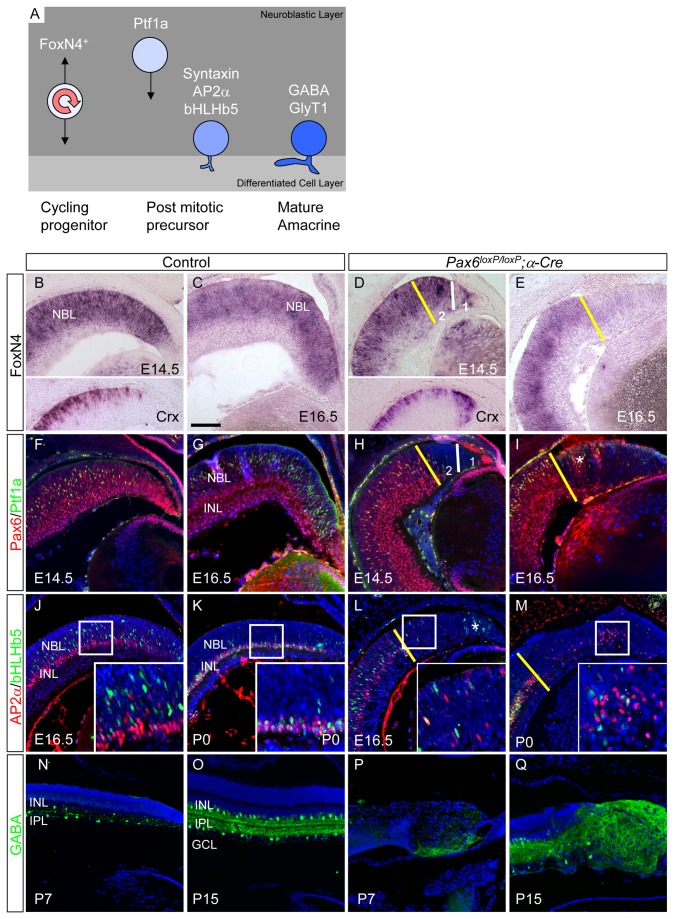
Figure 1. Delayed differentiation of amacrine precursors in the Pax6 loxP/loxP ;α-Cre retina.
(A) A scheme of the stages of amacrine interneuron differentiation. Amacrine cells evolve from FoxN4-expressing RPCs. In the postmitotic amacrine precursors, FoxN4 is reduced and Ptf1a expression is initiated. The Ptf1a-positive precursors migrate to the prospective INL, lose Ptf1a expression and initiate expression of TFs involved in the differentiation of amacrine subtypes (e.g. Ap2α and bHLHb5). The final differentiation of amacrine cells occurs a few days after birth with accumulation of neurotransmitters and transporters (e.g. GABA, glycine transporter GlyT1). Expression of amacrine specification and differentiation markers in control (B,C,F,G,J,K,N,O) and Pax6loxP/loxP;α-Cre OC (D,E,H,I,L,M,P,Q). Expression of FoxN4 (B–E, the inset in B and D is Crx on adjacent section) as detected using ISH. Indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) was employed to detect the expression of Ptf1a and Pax6 (green and red, respectively, F–I; adjacent sections to B-E respectively), bHLHb5 and Ap2α (green and red, respectively, J–M) and GABA (green, N–Q) during various stages of development as indicated. Pax6 (red in F–I and not shown) and Crx (inset in B,D and not shown) expression determined by IIF or ISH was used to identify the Pax6-deficient area (yellow line in D,E,H,I,L,M) and to delineate the neurogenic and nonneurogenic RPC populations in the Pax6 loxP/loxP;α-Cre retina (numbered 1 and 2 and separated by a dotted white line in D and H). Abbreviations: GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; NBL, neuroblastic layer. Scale bar in C is 100 µm.