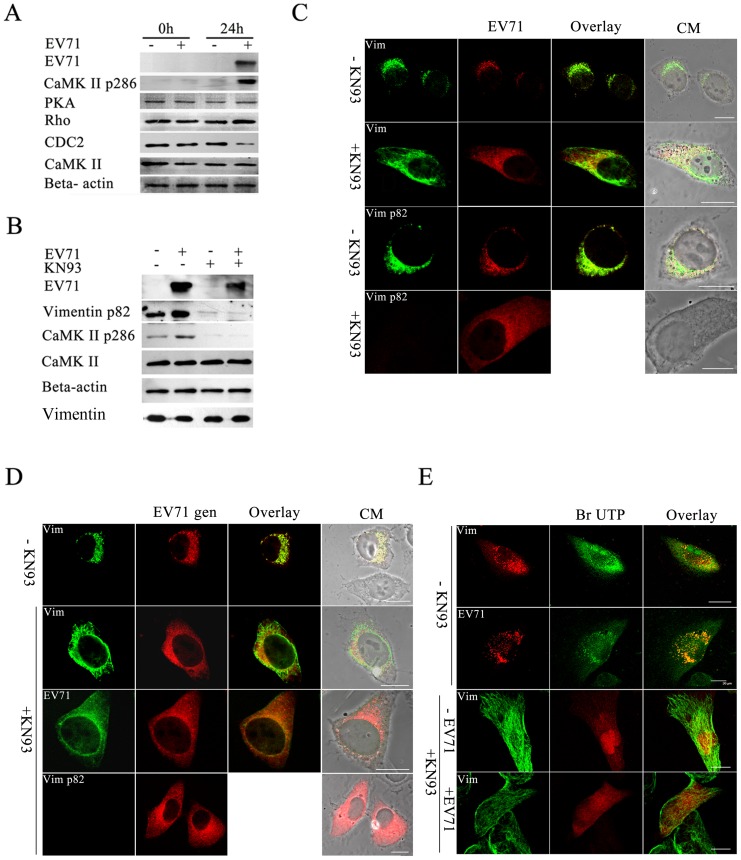
Figure 5. Analysis of CaMK-II activation and its roles in EV71 infection.
(A) Western blot analysis of EV71 infected U251 cells showing the activation of CaMK-II during EV71 infection. Cell infected with EV71 (+) or mock infected (−) and incubated for 24 h (24 h) or unincubated (0h), respectively, were lysed and immunoblotted with antibodies against either PKA, CDC 2, Rho-kinase (Rho), CaMK-II, phosphorylated CaMK-II (CaMK-II p286), EV71 or Beta-actin internal control as shown on the left. The results showed that only an increase in the expression of CaMK-II p286 was detected after infection with EV71. (B) Western blot detection of CaMK-II p286, CaMK-II, EV71 VP1 and ser 82-p vimentin protein levels in cells treated with KN93. Infected (+ EV71) and uninfected U251 cells (− EV71) were incubated in the presence (+ KN93) or absence of KN93 (− KN93) and processed for western blot with antibodies against CaMK-II, phosphorylated CaMK-II (CaMK-II pThr 286), ser 82-p vimentin (Vimentin p82), EV71 and Beta-actin (internal control) as described in Materials and Methods. Total vimentin in cells was also analyzed. The antibodies used is labelled on the left. The figure shows the levels of CaMK-II Thr 286 phosphorylation, vimentin Ser-82 phosphorylation and EV71 proteins were decreased in the presence of KN93. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of the distribution of vimentin (Vim), ser 82-p vimentin (Vim p82) and EV71 protein (EV71) in EV71 infected cells in the presence (+KN93) or absence of KN93 (− KN93) as described in Materials and Methods. The figure shows the fluorescence observed after treatment with the respective antibodies. The figure shows the aggresomes found in KN93 untreated cells disappeared after KN93 treatment. Bar: 20 μm. (D) FISH analysis of the effects of KN93 on vimentin aggresomes formation. U251 cells were infected with EV71 and treated (+ KN93) or untreated with KN93 (−KN93), and hybridized with DNA probe, followed by staining with antibodies to vimentin (Vim), ser 82-p vimentin (Vim p82) and EV71 (EV71), and subjected to confocal microscopy analysis as described in Materials and Methods. The figure shows the red fluorescence representative of the EV71 genome (EV71 gen) observed after DNA hybridization and the green fluorescence observed after blotting with the respective antibodyand an overlay of the two. CM: Cell morphology. Bar: 20 μm. (E) Analysis of the effect of KN93 on the distribution of newly synthesized viral RNA, vimentin and ser 82-p vimentin in viral infected cells. Cells were infected with EV71 and treated (+KN93) or untreated (−KN93) with KN93 as described above. The incorporated BrU to RNA was detected using a mouse anti-BrdU antibody (BrU) and is observed as fluorescence on the middle column. After washing, cells were stained with antibodies to EV71, vimentin (Vim), and serine 82-p vimentin (Vim p82) and the positive signals are observed as fluorescence on the left column.An overlay of the two are shown in the right column. CM: Cell morphology. Bar: 20 μm.