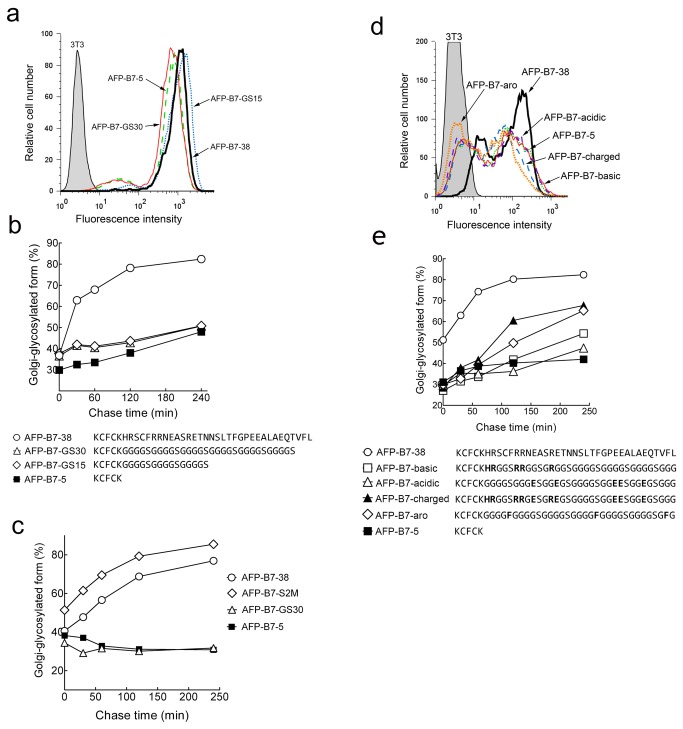
Figure 14. Intracellular transport rates of AFP chimeric proteins with flexible cytoplasmic domains.
a) Non-structured cytoplasmic tails were generated by appending GGGGS repeats of 15 or 30 residues to AFP-B7-5 to generate AFP-B7-GS15 or AFP-B7-GS30, respectively. The expression of AFP-B7-38, AFP-B7-GS15, AFP-B7-GS30 and AFP-B7-5 on the surface of stably transfected 3T3 cells was determined by flow cytometry. b) The percentage of intracellular Golgi-glycosylated AFP chimeric protein relative to total intracellular AFP chimeric protein as a function of time is shown. c) The percentage of intracellular Golgi-glycosylated AFP chimeric protein relative to total intracellular AFP chimeric protein as a function of time is shown in stably transfected HEK293 cells. d) The basic (AFP-B7-basic), acidic (AFP-B7-acidic), charged (AFP-B7-charged) or aromatic (AFP-B7-aro) amino acids present in the B7 cytoplasmic domain were introduced into the same positions in a chimeric protein possessing GGGGS repeats in the cytoplasmic tail. The expression of chimeric proteins on the surface of transiently-transfected 3T3 cells was determined by flow cytometry. e) The percentage of intracellular Golgi-glycosylated AFP chimeric protein relative to total intracellular AFP chimeric protein as a function of time is shown.