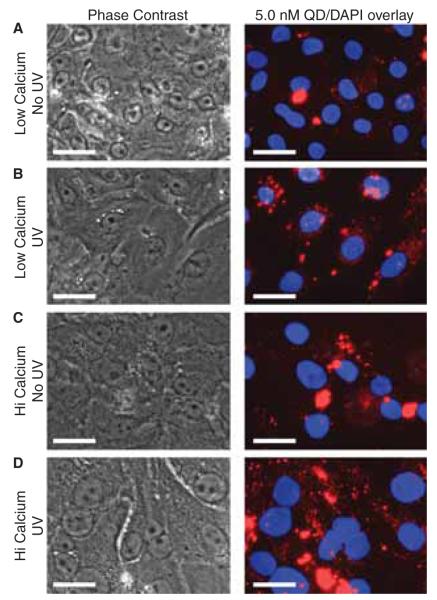
Figure 4.
Phase contrast and fluorescent microscopy images of the QD-cell interactions. Primary keratinocytes cultured in high- and lowcalcium conditions were either irradiated with 40 mJ cm−2 UVB or sham irradiated and incubated with 5.0 nM QD. After 24 h the media was removed and replaced with 1x DPBS to allow imaging in the plate. UVB appeared to increase the uptake of QDs in keratinocytes cultured in low-calcium conditions (A, B). In high-calcium conditions, there is an increased presence of QD clusters (C, D) which make it difficult to discern an effect of UVB. Control studies indicate that highcalcium conditions do not exacerbate the precipitation of QDs thus suggesting an increased association with the differentiated keratinocyte phenotype. Scale bar = 25 μm.