Figure 5. Ability of LOS·MD-2[125I] to detect and analyze limited human TLR4 binding sites in a stable HEK293 cell line.
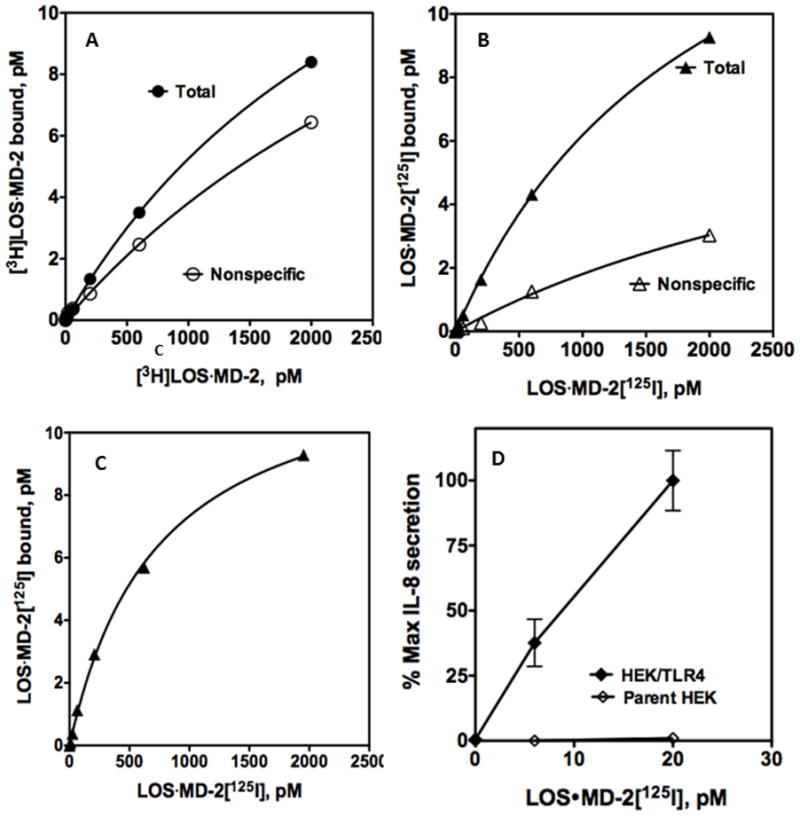
Binding of increasing concentrations of [3H]LOS·MD-2 (A) or LOS·MD-2[125I] (B) to HEK293 cells stably expressing TLR4 or HEK parent cells (2 million cells/sample) during 30 min incubation at 37°C. Specific TLR4-dependent binding of LOS·MD-2[125I] was calculated as the difference between total and non-specific cpm bound (C). Scatchard analysis of the data by GraphPad Prism was used to determine Kd and Bmax: Kd = 734 ± 40 pM and Bmax= 12.7 ± 0.3 pM for binding of LOS·MD-2[125I] to HEK/TLR4. Data are a composite of more than three experiments, each dose done in duplicate. (D) Dose-dependent cell activation by LOS·MD-2[125I] of HEK/TLR4 or parent HEK cells was measured as extracellular accumulation of secreted IL-8 by ELISA as described in Materials and Methods. Data shown are representative of one experiment with duplicate samples for each dose and are representative of more than three similar experiments. The dose curve of only low concentrations of LOS·MD-2 are shown to highlight the sensitivity of TLR4 activation by LOS·MD-2.
