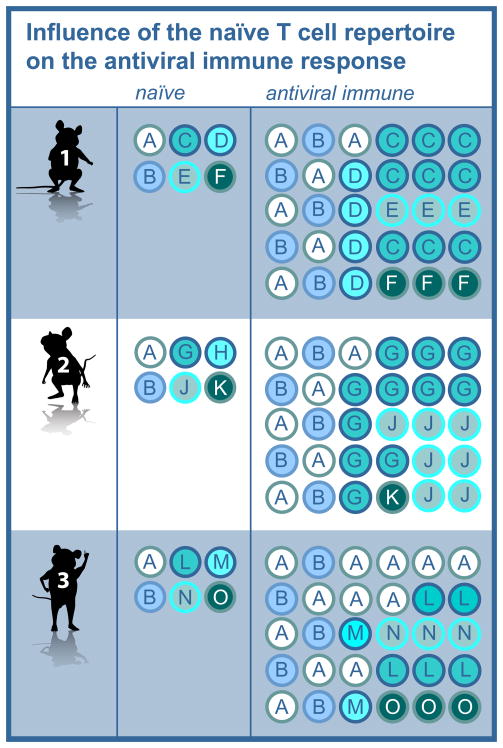
Figure 1. Influence of the naïve T cell repertoire on the antiviral immune response.
A schematic depicting the clonotypes present in the naïve and antiviral immune repertoires of three mice. Each letter corresponds to a unique clonotype. The antiviral immune repertoire broadly reflects the characteristics of the naïve repertoire, but for all epitopes shows significantly greater inequality in the distribution of clonotypes relative to the naïve repertoire, with some responses expand to a greater extent than others (e.g. clonotypes C, G, J and O). The extent of sharing is largely determined in the naïve repertoire (e.g. clonotypes A and B) and reflects sharing of both minor and dominant clones.