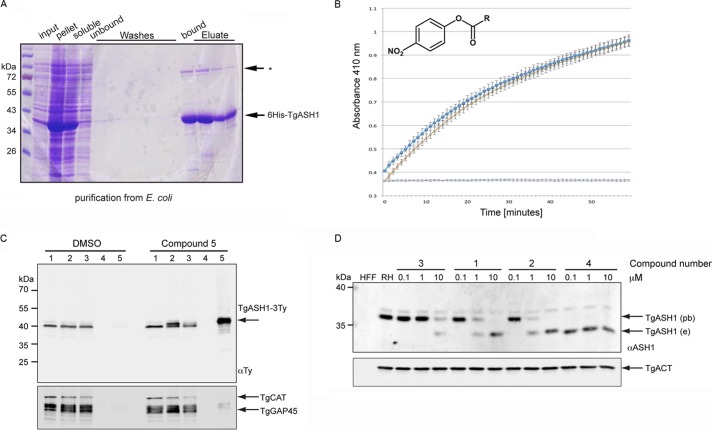
FIGURE 5.
TgASH1 has thioesterase activity and interacts specifically with APT1 inhibitors. A, purification of recombinant His6-tagged full-length TgASH1 from E. coli. Lysis was performed in 1% Triton X-100 with sonication. * indicates an unspecific band identified by the α-ASH1 Ab. B, TgASH1 hydrolyzes PNP-palmitate with activity comparable with that of human APT1. The detection is based on the absorbance measurement associated with release of PNP (measured at 410 nm). Dark blue squares represent TgASH1, light blue crosses with an orange line represent hAPT1. The light blue line is the control without protein. C, pulldown of inhibitor targets with compound 5, a clickable compound modified to accept biotin, indicates a specific interaction between the inhibitor compound and TgASH1 as shown by Western blot. TgASH1-3Ty parasites were incubated with compound 5 to allow it to bind to its protein targets. Following precipitation of proteins and performing the click reaction to add the biotin to the compound 5-target complex, inhibitor targets were enriched on streptavidin beads and analyzed by Western blot. TgGAP45 and catalase (TgCAT) were used as negative controls, and a second sample that was treated with DMSO only instead of compound 5 was run. Numbers 1–5 represent the different fractions: 1, input; 2, precipitated proteins; 3, postclick reaction sample; 4, wash; 5, eluate. D, FP-Rh binds specifically to TgASH1, increasing its size and causing it to migrate more slowly on SDS-PAGE. Western blot analysis demonstrates the shift of endogenous TgASH1 (TgASH1e) bound to the probe (TgASH1pb). In the presence of an increasing concentration of inhibitors that interfere with binding to the probe, migration reverts back to the size of unbound TgASH1-3Ty. Actin (TgACT) was used as loading control. RH, wild type parasite line.