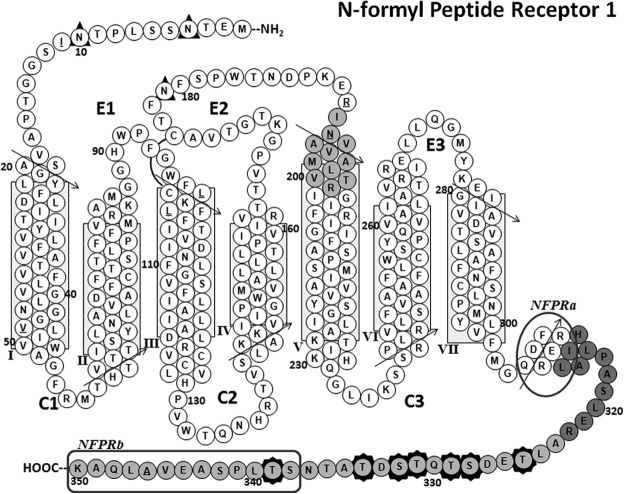
FIGURE 7.
FPR1 predicted transmembrane structure showing identified peptides and Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites. A “snake” diagram of the predicted transmembrane structure of FPR1 is shown. The tryptic peptides identified by mass spectrometry are shaded gray, and Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites are identified by seven darkly shaded star borders around amino acid residue circles. The extracellular loops are marked E1, E2, and E3, and the cytoplasmic loops are marked C1, C2, and C3. The predicted α-helical regions are shown as stacks of closely packed circles representing each type of amino acid residue, with arrows depicting the direction along which the sequences should be read. The predicted transmembrane region is boxed for helices I–VII. The predicted amphipathic helix VIII (67) is also shown. A putative disulfide bond between Cys98 and Cys176 is shown as an arc connecting the two residues. Underlined residues represent positions in the sequence for which normal SNP variants exist (17). These polymorphisms are I11T, V47L, L97M, L101V, R190W, N192K, and A346E. The phage display-mapped epitopes for each mAb are marked by a rounded rectangle for NFPRb and an oval for NFPRa showing specific C-terminal tail residues identified by the mapping. This model is based on a structural alignment of the FPR1 sequence on a template derived from superposition of several known x-ray crystal structures of GPCRs (human A2a adenosine receptor (73), human M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (PDB code 3UON) (74), CXCR4 chemokine receptor (PDB code 3ODU) (75), human histamine H1 receptor (PDB code 3RZE) (76), neurotensin nts1 receptor (PDB code 4GRV) (77), human dopamine receptor (PDB code 3PBL) (78), metarhodopsin 2 (PBD code 3PQR) (79), and the β-adrenergic receptor (PBD code 3SN6) (48)), using the homology modeling functions of Accelrys Discover version 3.5.