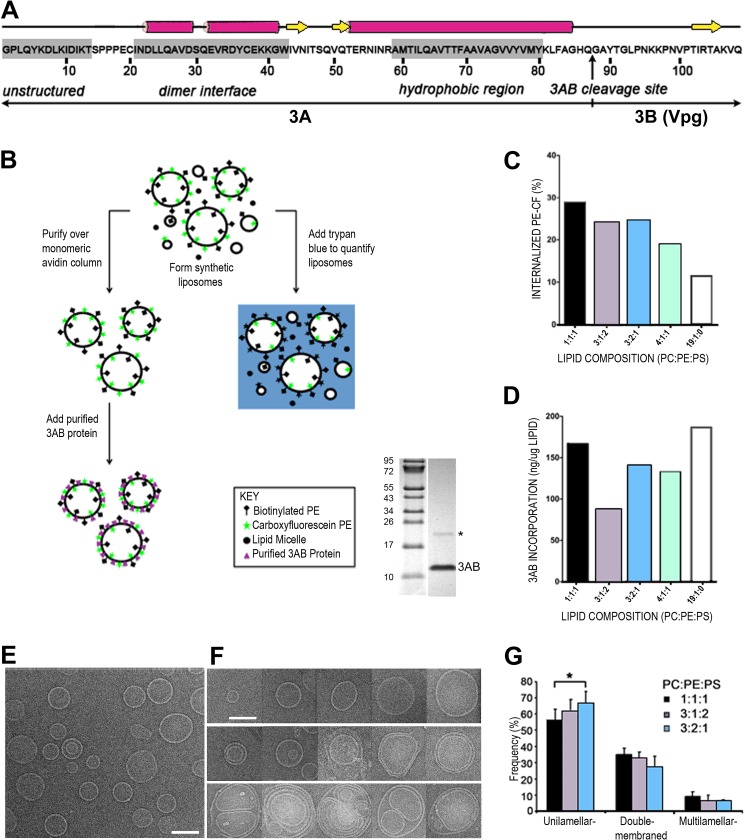
FIGURE 1.
Synthesis and characterization of synthetic proteoliposomes containing purified poliovirus 3AB protein. A, the sequence of the stable precursor protein 3AB encoded by poliovirus is shown, with the vertical arrow denoting the Gln/Gly cleavage site between the 3A and 3B proteins. The unstructured N terminus (30), dimerization interface, and the membrane association domain of 3AB (38) are highlighted by gray shades. B, flow chart of liposome formation, quantitation, and recruitment of purified 3AB protein. The gel shows the purity of 3AB, and the asterisk marks the dimeric form of 3AB. C, quantitation of liposome formation from a representative experiment. Five different lipid compositions were tested: 1:1:1, 3:1:2, 3:2:1, 4:1:1, and 19:1:0 PC:PE:PS. Trypan blue was used to quench the fluorescently labeled PE in lipid micelles and in the outer leaflet of the lipid bilayer of liposomes. The remaining, topologically sequestered fluorescence was quantified to estimate the liposome formation. CF, carboxyfluorescein. D, 3AB reconstitution was quantified by measuring the amount of 3AB in the lipid bilayer after isolation of proteoliposomes by ultracentrifugation. The amount of lipid was quantified by fluorimetry, and 3AB protein was quantified by immunoblot analysis and densitometry. E, micrograph of liposomes composed of 3:2:1 PC:PE:PS. Scale bar = 100 nm. F, representative images of unilamellar (top row), double-membraned (center row), and multilamellar (bottom row) liposomes of different sizes. Liposomes were composed of 3:2:1 PC:PE:PS. G, affinity-purified liposomes of the indicated compositions were visualized by cryo-EM, and the number of single-, double-, and multimembraned liposomes was quantified. The asterisk denotes a statistically significant difference.