FIGURE 8.
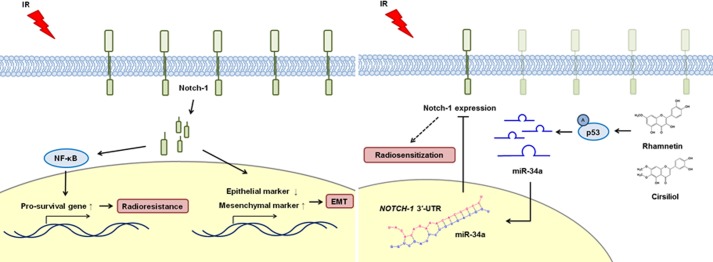
Schematic diagrams illustrating Notch-1 signaling in response to irradiation and the radiosensitizing effects of rhamnetin and cirsiliol in NSCLC cells. Irradiation induced Notch-1 overexpression specifically in NSCLC cells and not in normal lung cells or tissues. Treatment with rhamnetin or cirsiliol also reduced the proliferation of NSCLC cells through the suppression of radiation-induced Notch-1 expression. Additionally, rhamnetin and cirsiliol increased the expression of miR-34a (tumor-suppressive miRNA) in a p53-dependent manner in the cells. Reduced Notch-1 expression increased NSCLC cell apoptosis through significant down-regulation of NF-κB signaling. Finally, EMT induced by radiation was notably attenuated in the presence of rhamnetin and cirsiliol in the NSCLC cells. These results demonstrated that two flavonoids, rhamnetin and cirsiliol, can act as novel radiosensitizers to enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy by inhibiting irradiation-induced Notch-1 expression and its signaling pathways associated with radioresistance.
