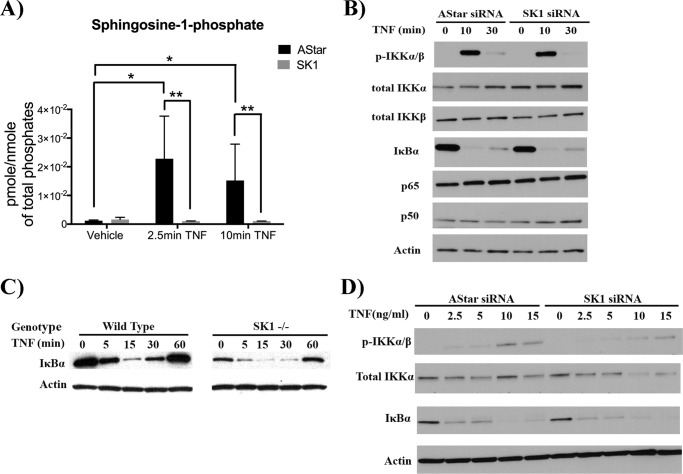
FIGURE 3.
SK1 is dispensable for TNF-mediated activation of NF-κB. A, HeLa cells were treated with 20 nm Astar or SK1 siRNA for 48 h prior to treatment with TNF (20 ng/ml) or PBS for 2.5 and 10 min. Cellular lipids were directly extracted in organic solvent extraction, and S1P levels were analyzed by tandem LC/MS mass spectrometry. Lipid levels were normalized to nmol of total. The data represent means ± S.E. of two independent experiments performed in duplicate. B, HeLa cells were treated with 20 nm Astar or SK1 siRNA for 48 h prior to treatment with TNF (20 ng/ml) for 0, 10, or 30 min. Early downstream signals of TNF including IKKα/β phosphorylation and IκBα degradation were examined via immunoblot. The total levels of NF-κB subunits p65 and p50 were also analyzed. Actin was included as a loading control. Each blot is representative of three independent experiments. C, MEFs derived from WT or SK1−/− mice were treated with 4 nm TNF for 0, 5, 15, 30, or 60 min, and IκBα levels were assessed by immunoblot with actin as a loading control; blots are representative of three independent experiments. D, HeLa cells were treated with 20 nm Astar or SK1 siRNA for 48 h prior to treatment with various TNF doses as indicated for 10 min 2.5, 5, 10, or 15 ng/ml TNF were added for 10 min. IKKα/β phosphorylation and IκBα degradation were examined via immunoblot with actin as loading controls. Each blot is representative of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.